How to Increase PHP Limits
How do you increase PHP limits? PHP has a default limit of 50 MB (megabytes) set for uploading through PHP scripts on our servers. If you need to upload files larger than this limit, you can increase it by editing the php.ini file. This article will guide you through updating the upload limits via php.ini.
Changing the php.ini file in your account will not impact the phpMyAdmin tool in cPanel. This is because phpMyAdmin uses a different php.ini file that is accessible only to the server administrators. To begin, log in to your Bluehost account.
Editing upload_max_filesize and post_max_size
- Log in to your Bluehost Portal.
- Click Hosting in the left-hand menu.
- Click the File Manager button.
You can access the public_html folder if you are working on the primary domain of your account, or access the root - folder with the name of the specific addon domain you'd like to work on. These folders usually house your php.ini file.
- Scroll down in the right-hand panel to the file php.ini and right-click it.
- In the pop-up menu, select Edit.
- Use the keyboard shortcut to open the find pop-up window.
Windows and Linux: Ctrl + f
Mac: Command (⌘) + f - Find the upload_max_filesize setting, type it into the search bar, and hit enter.
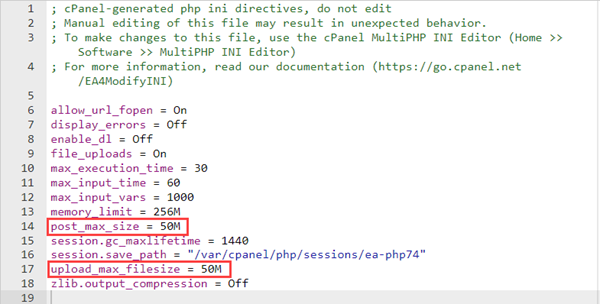
- Increase the maximum file size that can be uploaded, look for the line upload_max_filesize = 50M, and change the value 50M to the desired size.
- Open the find pop-up and type post_max_size in the Search field. Press enter.
- Highlighted will be post_max_size = 50M. It must be changed to the same number entered for upload_max_filesize.
- To save the changes, please click on the Save button.
memory_limit
When the PHP engine handles an incoming POST, it must keep some of the incoming data in memory. This directive only affects if you have used the --enable-memory-limit option during configuration. Setting too high a value can be very dangerous, as several uploads being handled concurrently can lead to memory limits maxing out and server performance issues.
max_execution_time and max_input_time
These settings define the script's maximum lifetime and the time the script should spend accepting input. If several megabytes of data are transferred, max_input_time should be reasonably high.
Apache Settings
The Apache web server has a LimitRequestBody configuration directive that restricts all POST data sizes, regardless of the web scripting language in use. Some RPM installations set the limit request body to 512Kb. You must change this to a larger value or remove the entry altogether.
Other Options
If you expect to handle many concurrent file transfers on your website, consider using a PERL or Java server-side component. PHP is our favorite web programming language, but PERL can offer a slight advantage when handling files.
Most installations of PERL as an Apache module can accept up to 32 megabytes out of the box. Compare this against the 2MB default for PHP. The downside is that PERL coding takes more effort than PHP, but it's worth it.
Summary
If you need to upload files larger than the default limit of 50 MB set for uploading through PHP scripts on your servers, you can increase it by editing the php.ini file. Following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily increase PHP limits via php.ini. Remember to set your PHP in the cPanel to one of the Single php.ini options to accomplish this task. Additionally, be mindful of the various settings, such as memory_limit and max_execution_time, that can affect the performance of your server. If you encounter any issues or have further questions, don't hesitate to contact support for assistance.
If you need further assistance, feel free to contact us via Chat or Phone:
- Chat Support - While on our website, you should see a CHAT bubble in the bottom right-hand corner of the page. Click anywhere on the bubble to begin a chat session.
- Phone Support -
- US: 888-401-4678
- International: +1 801-765-9400
You may also refer to our Knowledge Base articles to help answer common questions and guide you through various setup, configuration, and troubleshooting steps.