Key highlights
- Streamline development by using Git with WordPress to track changes, collaborate efficiently and maintain clean version control.
- Improve workflow by connecting GitHub to WordPress, making it easier to manage updates and keep your project organized.
- Set up and test safely with WordPress with GitHub workflows that let you experiment locally before pushing changes live.
- Enhance productivity through seamless WordPress GitHub integration that simplifies syncing, backups and team collaboration.
- Boost code management using GitHub for WordPress to store repositories securely and support smooth theme and plugin development.
Sharing your creations is often appreciated and the same idea is reflected in WordPress development. When something new is built for WordPress, the desire to share it with the community is naturally felt. If free hosting for custom code is being considered, using Git with WordPress or connecting WordPress with GitHub may be seen as an ideal approach.
Git and GitHub offer powerful version control for managing your codebase, from your GitHub repository to your local repository and your overall WordPress development workflow.
They let you host your work, collaborate with others and keep everything organized through simple updates to your repository page or local repository folder. You can even use GitHub Pages for free hosting if you’re deploying a static WordPress site.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to use GitHub to WordPress and manage your WordPress themes and plugins with smooth WordPress GitHub integration.
What is Git?
Git, short for Global Information Tracker, is a distributed version control system designed to help you keep track of changes in coding projects or files. These projects are stored in a repository, often called a repo, which is essentially a parent folder Git uses to organize all the files it is managing.
This is also the foundation when you use WordPress with GitHub or set up WordPress GitHub integration for your projects.
Git is a go-to tool for developers working on various software projects. One of its biggest advantages is that multiple people can create their own clones of the main repository, which contains the original code.
They can then make edits or changes on their own local machine without directly altering the main repo.
This is helpful for workflows like Using Git with WordPress or preparing code that will connect GitHub to WordPress or be part of GitHub for WordPress development.
Once the changes are ready to go live, users upload them to a service like GitHub, which helps keep the team’s repositories organized and accessible.
Git vs. GitHub
Many beginners assume Git and GitHub are the same, but this comparison table shows how different they actually are.
Understanding this difference is important before setting up any workflow whether you’re Using Git with WordPress, managing a WordPress GitHub integration or pushing theme updates from GitHub to WordPress.
Git vs GitHub comparison
| Feature | Git | GitHub |
| Type of tool | Version control system | Web hosting platform for Git repositories |
| Primary function | Tracks changes in your code and organizes it into repositories | Stores Git repositories and makes them accessible online |
| Usage environment | Works locally on your machine | Works online in the cloud |
| Dependency | Can be used independently | Requires Git to function |
| Collaboration | Limited to local development unless connected to a remote platform | Built-in collaboration tools for teams and remote contributors |
| Interface | Command-line based | User-friendly web interface |
| Security and backup | Dependent on your local machine | Cloud storage keeps your code safe even if your device is lost or damaged |
| Alternative competitors | Not applicable | Competes with platforms like Launchpad, Assembla and Bitbucket |
From above, we can say that Git and GitHub are different tools. Git is the version control system that tracks changes in your code and organizes them into repositories, including those used when Using Git with WordPress or working on WordPress with GitHub projects.
GitHub is the platform that hosts these Git repositories and makes them accessible for teams managing GitHub to WordPress workflows or handling a GitHub repository for WordPress development.
Git can be used locally in a local repository, while GitHub depends on Git to store and sync your work. GitHub also offers helpful collaboration features and a user-friendly interface that supports WordPress GitHub integration and shared coding tasks.
Because GitHub stores everything in the cloud, your code remains safe even if your local machine is damaged or lost. This is especially useful when working with GitHub for WordPress setups for themes, plugins or development projects.
What are the prerequisites for using git with WordPress?

Before you start integrating Git with your WordPress projects, it is essential to ensure you have the right tools and basic knowledge.
Here’s what you need to work smoothly with Using Git with WordPress, WordPress with GitHub, WordPress GitHub integration and related workflows.
1. Basic command-line knowledge
Familiarity with command-line interfaces like Terminal on macOS/Linux or Command Prompt/PowerShell on Windows is important. You will use CLI commands to interact with Git, navigate directories using cd, list files with ls or dir and run basic Git commands that support your local repository and GitHub repository setup.
2. Git installed on your local machine
Check if Git is installed by running git –version. If it is not available, download it from the official Git site and follow the installation steps for your operating system. This is necessary before connecting your work to GitHub for WordPress or syncing GitHub to WordPress projects.
3. Local WordPress installation
Set up a local server environment using MAMP, XAMPP, WampServer or Local WP. Then install WordPress locally. This gives you a safe environment for WordPress development before pushing changes to your GitHub repositories.
4. GitHub account
Create a free GitHub account and learn how to create a new GitHub repository, commit changes and navigate the GitHub interface. This will help you manage your project when working with WordPress GitHub integration.
5. Text editor or IDE
Use a code editor like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text or an IDE such as PhpStorm to work on your WordPress files, themes and plugins.
6. Basic understanding of WordPress file structure
Know where themes (wp-content/themes/) and plugins (wp-content/plugins/) are located in the WordPress folder. A basic understanding of core WordPress files helps prevent accidental edits when syncing your local repository folder with GitHub.
Familiarity with PHP and general WordPress development practices is helpful, although not required, when using Git to manage your WordPress projects.
What are the benefits of using Git and GitHub with WordPress?
If you’re working on WordPress development, you’ve likely faced the frustration of managing different versions of your theme or plugin.
Maybe you’ve made updates and want to keep track of changes or you’re collaborating with others and need a streamlined way to manage contributions.
This is where Git and GitHub become useful for using Git with WordPress and maintaining a clean WordPress with GitHub workflow.
1. Version control
Git allows you to track changes to your files, keep a history of modifications, easily roll back to previous versions and collaborate without chaos. This is especially helpful when setting up WordPress GitHub integration for your project.
Example: If a new CSS change breaks your homepage layout, you can revert to the previous working commit instantly.
2. Backup security
GitHub safely backs up your code in multiple locations, so you do not have to worry about losing important data. This also supports long-term GitHub for WordPress development.
Example: Even if your laptop crashes, your entire WordPress theme repository remains safely stored on GitHub.
3. Effortless sharing
Sharing your code becomes simple, whether you are working on open-source projects or collaborating with a private team. This is useful when pushing updates from GitHub to WordPress or syncing your work in a GitHub to WordPress setup.
Example: A teammate can clone your GitHub to WordPress plugin project and start contributing within minutes.
4. Smooth team collaboration
GitHub streamlines teamwork by allowing seamless contributions from multiple developers on the same project.
Example: Two developers can work on different features at the same time and merge changes without overwriting each other’s files.
5. Build connections
Working on GitHub helps you connect with other developers and expand your professional network.
Example: Developers often discover your project through GitHub stars, issues or pull requests and reach out for collaboration.
6. Enhance your profile
GitHub is also a great way to showcase your work and build a professional portfolio others can view.
Example: Recruiters frequently check GitHub profiles to evaluate real code samples from WordPress developers.
7. Professional development workflow
Using Git and GitHub helps you manage your WordPress development workflow in a more structured and professional way.
Example: Your project gains a consistent workflow where every update, bug fix or new feature is documented through commits.
How to use Git and GitHub for WordPress development?
Git and GitHub are invaluable tools for WordPress theme and plugin development. Whether you’re creating a new theme or customizing an existing one, GitHub offers an effective platform for managing your project’s codebase.
This applies to any workflow involving Using Git with WordPress, WordPress with GitHub or setting up WordPress GitHub integration.
For example, when you’re developing a custom theme for your site, you can fetch the theme repository from GitHub, make your changes and test everything on a local server.
Once you’re satisfied with the updates, you push the updated repository to GitHub and then apply those changes to the live WordPress website. This kind of workflow also supports GitHub to WordPress updates when syncing changes to your site.
The same process applies to plugin development. If you’re a WordPress developer building a plugin, GitHub helps you manage the codebase efficiently. This is especially useful for open-source projects, where other developers can contribute by fixing bugs or adding enhancements.
You can download the plugin files from GitHub, improve them and share your work with the community, which strengthens your overall GitHub for WordPress workflow.
Aside from managing development, GitHub can also be used to download and install WordPress plugins and themes on your live website.
However, it is important to remember that while GitHub supports storing and downloading files, it is not designed to function as a storage service like Dropbox or Google Drive.
Setting up a local WordPress environment for Git
Before diving into Using Git with WordPress, it’s best practice to create a local WordPress environment. This lets you safely work on your project, make changes, test new code and develop plugins or themes without affecting your live site.
If something breaks, you can easily debug issues locally before deploying updates through your WordPress GitHub integration.
To set up a local environment, you’ll need software that lets you host a WordPress site directly on your computer instead of a live or staging server. Tools like Local WP, MAMP, XAMPP and WampServer are all excellent options.
They’re free, user-friendly and simple to set up, making them ideal whether you’re connecting GitHub to WordPress, working on WordPress with GitHub or preparing your next push to GitHub for WordPress development workflows.
Installing Git locally and creating a Git repository
Once your local WordPress environment is all set up, the next step is to install Git on your computer. However, before diving into the installation, it’s a good idea to check if Git has already been installed. If you’re using a macOS or Linux device, chances are you will find Git pre-installed.
To check, open the Terminal (on Mac or Linux) and type the command:
“git --version”On Windows, you can check by opening the Command Prompt and entering the same command:
“git --version”If Git is already installed, you’ll see its version number displayed. If not, you’ll see nothing or get an error message saying the command is unknown. In that case, you’ll need to install Git manually.
To install Git, take the following actions:
Step1: Go to the Git website.
Step 2: Navigate to the Downloads area.
Step 3: Choose the relevant download link based on your operating system (macOS, Windows or Linux). If you want to build from source, you will find tarballs on kernel.org.
- Launch the installation wizard after downloading.
- To finish the installation, click “Next” and adhere to the on-screen directions.
- Wait until Setup install Git into your system.
Note: To ensure that Git has been installed correctly, restart your terminal or command prompt after installation and type the following command:
“git --version” Now that Git is up and running, it’s time to create a local Git repository. This repository will allow you to commit changes to your WordPress files before pushing them to GitHub.
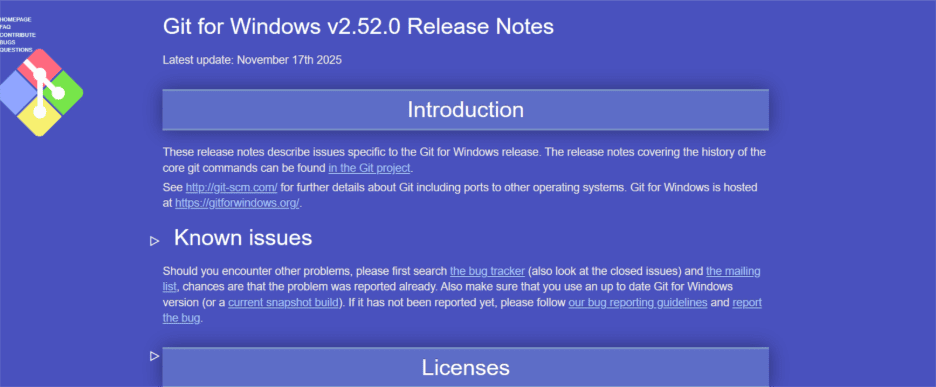
Here’s how you can create a local repository:
Step 1: Open your Bluehost dashboard and click on “Hosting” and then navigate “cPanel” at right side.
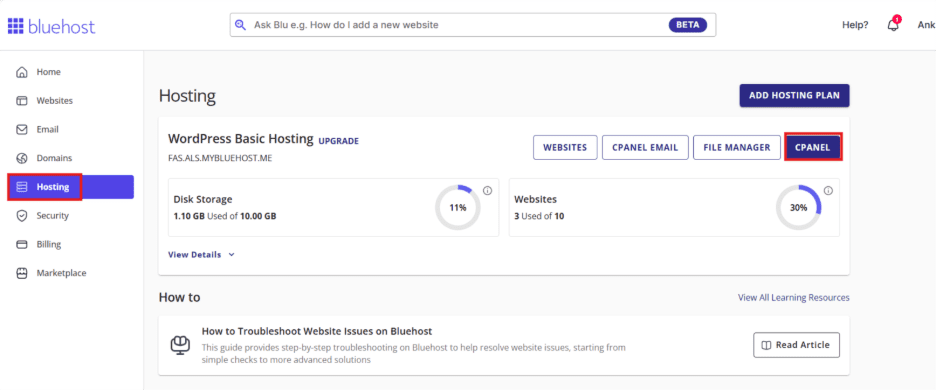
Step 2: Open cPanel and click on “File Manager” under “File” section.
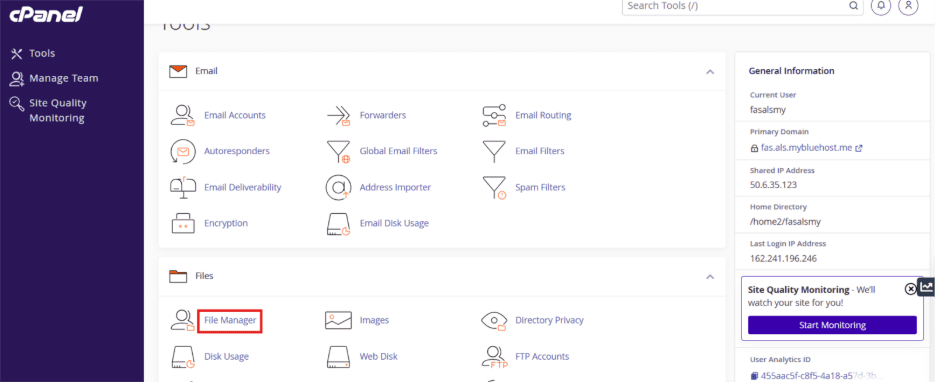
Step 3: Go to the wp-content folder and find the plugin or theme folder you’re working on.
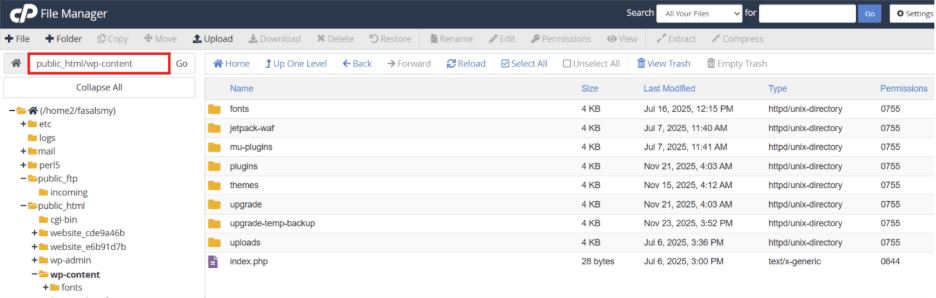
Step 4: Right-click anywhere inside that WordPress folder and select Open Git Bash Here (or open Git manually if you’re on Mac/Linux).
Step 5: In the terminal, type the following command to initialize a new Git repository:
“git init” 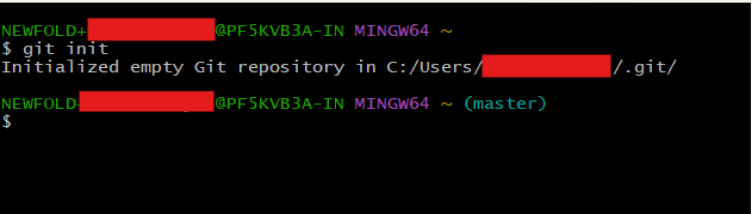
Step 6: Next, to stage all the files for your first commit, run this command:
“git add .” 
Step 7: Now, it’s time to commit your changes. You can add a commit message to explain what changes you’ve made:
git commit -m "your message here" Be sure to replace “your message here” with a relevant note about the updates you’ve made. Hit Enter to complete the commit.
After this, a hidden .git folder will appear in your local WordPress theme files or plugin files, indicating that your repository is set up and ready for version control.
Creating a GitHub repository and committing changes
The next step is to create a repository on GitHub to house your project after setting up Git locally. Here is how to take these actions:
Step 1: Visit the GitHub website and create a free account.
Step 2: You can create account using Google, Apple or email address. After inputting your details, click on “Create account”.
Step 3: On the next screen, you must fill in your details, such as your GitHub username, password and email preferences. GitHub will also ask you to solve a quick puzzle to verify your account, similar to reCAPTCHA.
Step 4: Once your account is set up, you’ll be taken to the GitHub dashboard. Look for the ‘+’ icon at the top right, click on it and select “New repository.”
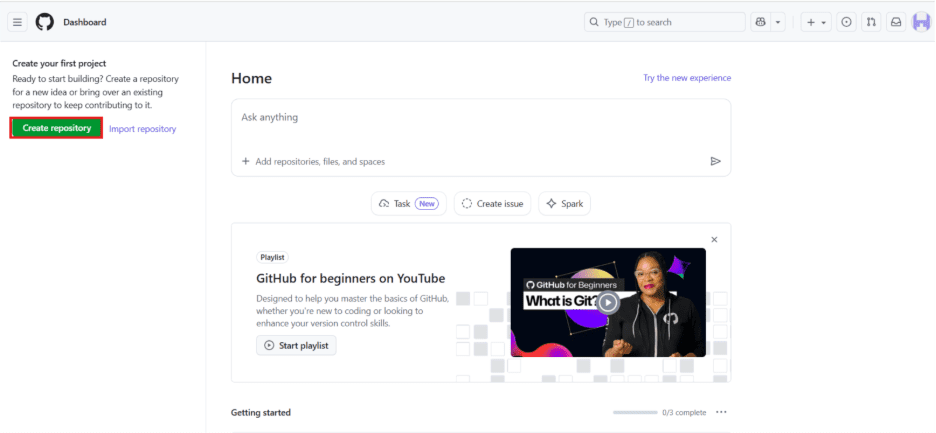
Step 5: Now that you’re creating a new repository, here’s what to do:
- Enter a name for your new repository. You can also add an optional description.
- Choose whether you want to make your repository public or keep it private.
- Scroll down and you’ll see more options, such as ‘ADD README’ file (which is great for documentation) and selecting a license for your project.
- Choose ‘Add .gitignore’ and ‘Add license’ options.
- Once you’ve filled in all the details, click the ‘Create repository’ button.
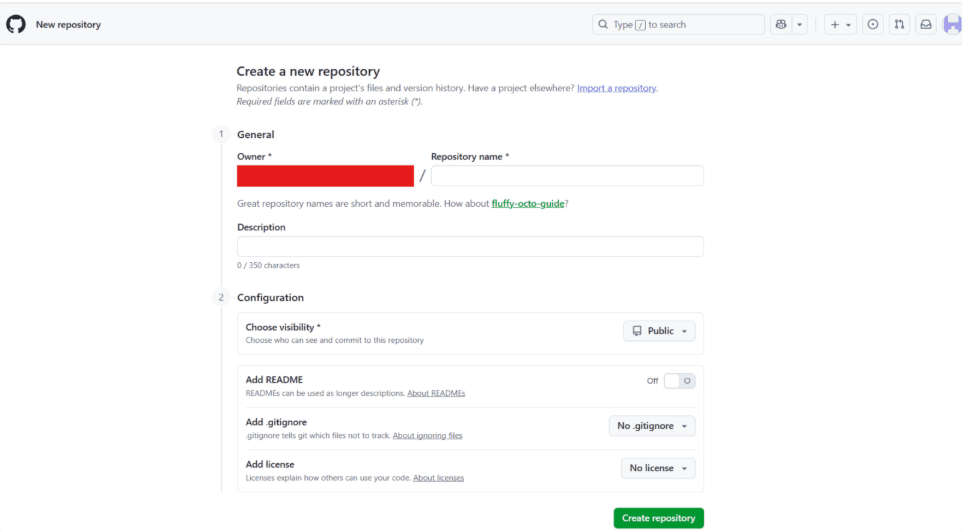
Step 6: You’ll get a link after the repository is created. This link will connect your local repository to the one you just created on GitHub. You can find the URL under the Quick Setup section.
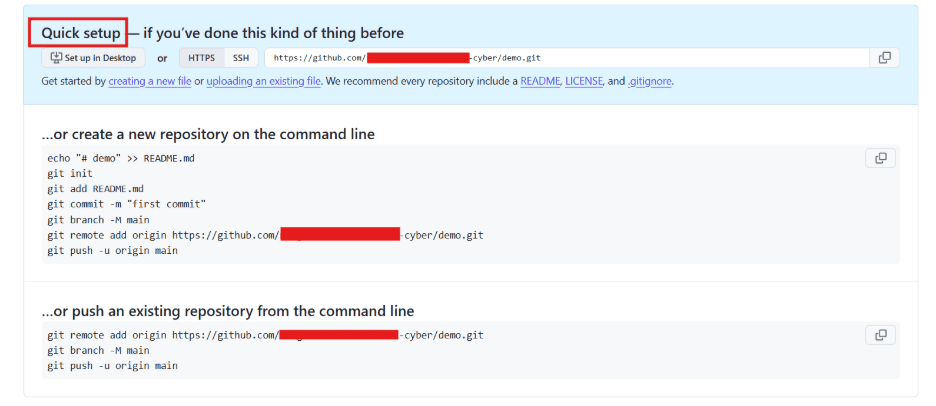
Step 7: To link your local repository with the GitHub repository, open Git Bash and run the following command, replacing the URL with your GitHub repository link:
“git remote add origin URL”
Step 8: After that, push your local files to GitHub by typing the following command:
“git push -u origin main” Note: If your GitHub account isn’t yet linked with Git, you’ll be prompted to sign in and authorize the connection. Once that’s done, your local files will be uploaded to GitHub, where they’re available for others to view and collaborate on.
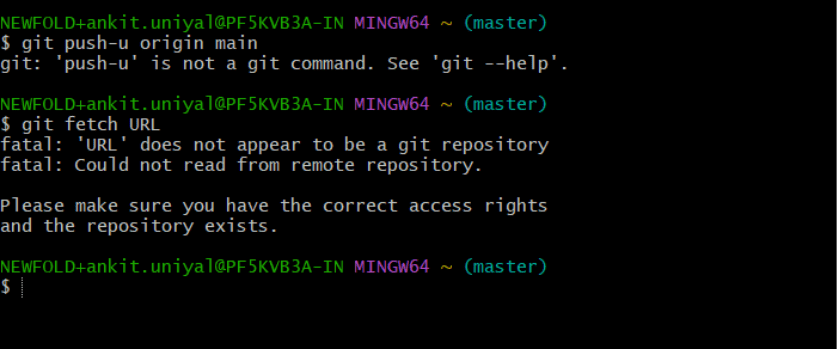
At this point, your repository on GitHub will display the files you’ve edited locally. Other developers can now fork, clone or contribute to your project.
If someone updates the repository, you can fetch the latest changes to your local environment by running the following command in Git Bash (again, replacing the URL with the GitHub repository link):
“git fetch URL” This ensures your local environment stays in sync with the latest updates from GitHub. Once you’re satisfied with your changes, you can push them to your live WordPress website.
Deploying GitHub themes and plugins to a live WordPress site
After completing the development of your WordPress plugin or theme, the final step is to deploy it on your live site.
While you can use Git commands to push updates to WordPress, there’s an easier way to use the WP Pusher plugin, which simplifies this process.
Here’s how you can deploy your project using WP Pusher:
Step 1: Head over to the WP Pusher website and click the “Download” button. Save the plugin files to your computer.
Step 2: Upload the theme from your local drive to WordPress.
Step 3: Now, upload the WP Pusher plugin. Click on ‘Upload Plugin’, then upload the zip file from your local disk.
Step 4: Next, install and activate the WP Pusher plugin in WordPress.
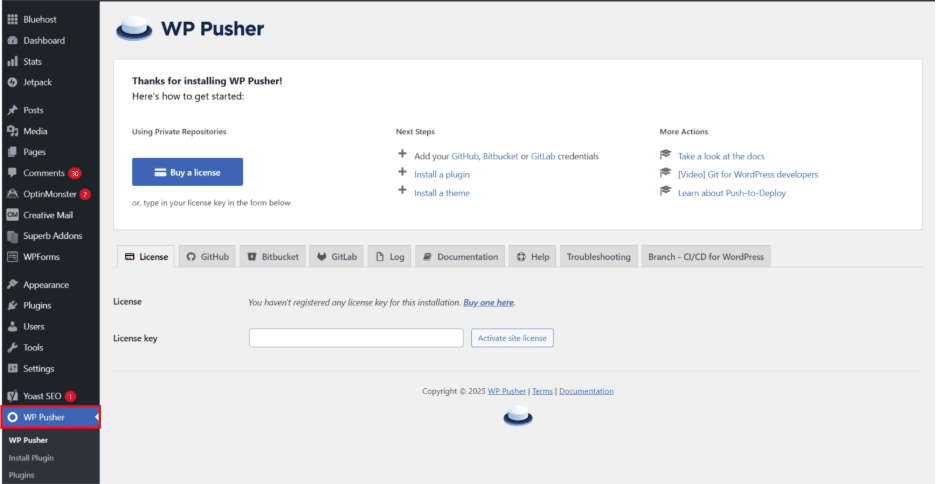
Step 5: Once WP Pusher is activated, navigate to the GitHub tab in the WP Pusher settings from your WordPress dashboard.
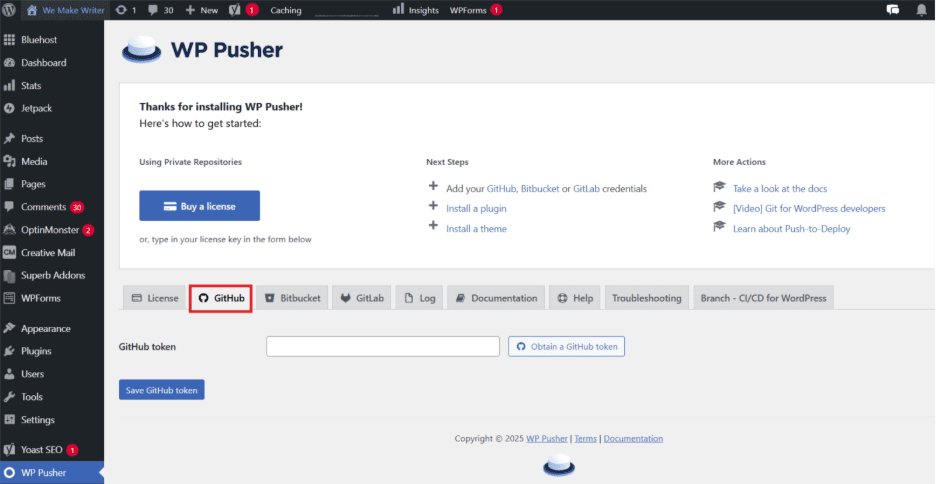
- A window requesting authorization to establish a connection to your GitHub account will show up. Click “Authorize WP Pusher” and log in to your GitHub account.
- After logging in, GitHub will generate a token for WP Pusher. Copy this token.
- In the WP Pusher settings, paste the token into the GitHub token field and click “Save GitHub token”. This creates a link between your GitHub account and WordPress website.
Now that GitHub is connected, you can deploy your themes and plugins directly from your GitHub repository.
Install plugins from GitHub:
Step 1: To install a plugin, navigate to WP Pusher » Install Plugin in the WordPress admin panel.
Step 2: Enter the plugin repository’s URL or click ‘Pick from GitHub’ to select the plugin from your GitHub account.
Step 3: After pasting the repository URL, you can specify additional options like the branch or subdirectory if needed.
Step 4: Scroll down and click ‘Install plugin’ to install it on your WordPress website.
Activate the plugin:
Step 5: After the plugin has been installed, select ‘Plugins’ > ‘Installed Plugins’ and click the newly added plugin by clicking ‘Activate’.
Step 6: At this point, your live site can utilize the plugin since it is active.
Install themes from GitHub:
- If you’re deploying a theme instead, follow the same process under ‘Install Theme’ in the WP Pusher menu.
- Enter the theme’s repository URL, fill in any necessary details and click ‘Install theme’.
With WP Pusher, managing and deploying custom themes and plugins from GitHub becomes seamless, allowing you to streamline the development process and ensure that your live WordPress site is always up to date with the latest changes.
How to install WordPress plugins and themes from GitHub?
Beyond using Git and GitHub for development, you can also source plugins and themes that are no longer available in the WordPress.org repository. Many WordPress developers maintain their plugins and themes on GitHub, making it a valuable resource when you can’t find them in the official library.
Here’s how you can install plugins and themes from GitHub:
Step 1: Open GitHub and search for the plugin or theme you want to install.
Step 2: Once you find the repository, click the ‘Code button’ and select ‘Download ZIP’. This will download a ZIP file containing the plugin or theme files to your computer.
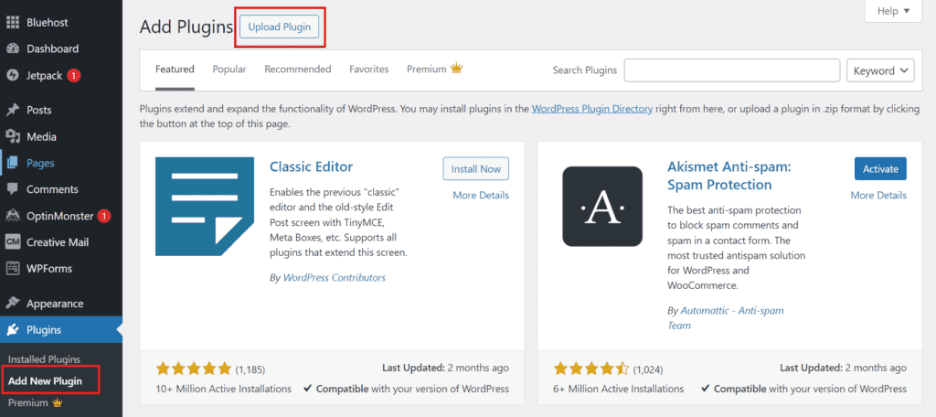
Step 3: To install the downloaded plugin or theme, go to your WordPress dashboard. For plugins, navigate to Plugins > ‘Add New Plugin’ and click ‘Upload Plugin’.
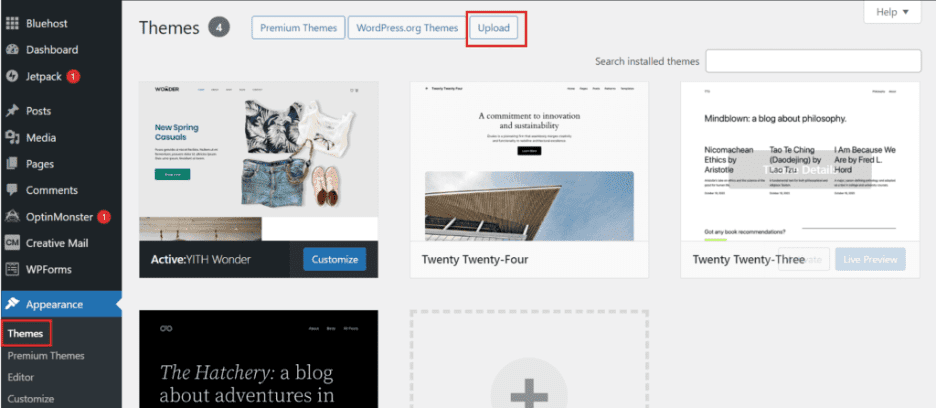
Step 4: For themes, go to Appearance > Themes and click ‘Add New’, then ‘Upload’. Choose the ZIP file you downloaded and install it.
Step 5: After installation, activate the plugin or theme from the respective sections in your WordPress dashboard. You can now use it on your site.
How to troubleshoot common Git issues in WordPress projects?
As a new developer working with WordPress, you might encounter a few common Git issues. Here’s a simple guide to help you troubleshoot and resolve these problems efficiently.
1. Merge conflicts
Issue: You encounter conflicts when merging branches.
Solution:
- Identify the conflicts: Git will point out which files are in conflict.
- Manually edit the conflicting files: Look for the conflict markers (e.g., <<<<<<< HEAD and >>>>>>>) and resolve them.
- Stage and commit the changes: Once resolved, use git add to stage the files, then commit the changes.
2. Accidentally committed sensitive files
Issue: Sensitive files (like passwords or API keys) were accidentally committed to your repository.
Solution:
- Remove the files: Use git rm –cached filename to remove the file from your Git history.
- Update your .gitignore: Add the sensitive files to .gitignore so they don’t get committed again.
- Remove them from your Git history: Use tools like BFG Repo-Cleaner to clean up past commits.
- Update any exposed credentials: Make sure to change any sensitive information that was exposed.
3. Synchronization issues
Issue: You encounter errors when trying to pull or push changes.
Solution:
- Use git pull –rebase: This ensures that your changes are reapplied cleanly on top of the latest commits.
- Avoid force-pushing: Only force-push when absolutely necessary, as it can overwrite others’ work.
- Check remote URLs: Make sure your remote repository URL is correct.
4. Detached HEAD state
Issue: You’re working in a “detached HEAD” state, meaning you’re not on a branch.
Solution:
- Create a new branch: Run git checkout -b branch-name to create and switch to a new branch.
- Switch to an existing branch: Use git checkout branch-name to get back to a branch you were previously working on.
5. Files in .gitignore still tracked
Issue: Git is still tracking the files you’ve added to .gitignore.
Solution:
- Untrack the files: Use git rm –cached filename to stop tracking the files.
- Check your .gitignore syntax: Ensure there are no mistakes in how you’ve listed the files in .gitignore.
6. Large repository due to media files
Issue: Your repository is getting too large because of media files.
Solution:
- Exclude media files: Add media files to .gitignore so they’re not committed.
- Use Git LFS: For large files, use Git Large File Storage (Git LFS) to store them more efficiently.
7. Line ending conflicts
Issue: You’re facing issues due to different operating systems using different line endings (e.g., Windows vs. Mac/Linux).
Solution
- Configure Git: Run git config core.autocrlf true on Windows to handle line ending differences.
- Standardize settings: Ensure your team uses consistent Git settings to avoid future line-ending conflicts.
Important Git and GitHub terms you should know
As you delve into using Git and GitHub for WordPress development, you’ll encounter several key terms. Here’s a quick glossary to help you navigate:
- Branches: Think of branches as separate paths within a repository. They allow you to make changes independently of the main codebase, so you can experiment without affecting the live version.
- Merge: Merging is the process of integrating changes from one branch into another. For example, you might merge a feature branch into the main branch to combine updates.
- Pull: Pulling involves fetching changes from a remote repository and incorporating them into your local copy. It ensures that your local files stay up to date with the latest changes.
- Pull requests (PR): One method to suggest modifications to a repository is through a pull request. Before the modifications are integrated into the main codebase, it enables others to examine and debate the changes.
- Fork: Forking creates a personal copy of another user’s repository. You can make changes to your fork without affecting the original project.
- Commit: A commit is a record of the modifications that have been made to the repository. Each commit has a unique ID and records who made the changes and when.
- Push: Pushing sends your local changes to a remote repository on GitHub, making them accessible to others.
Final thoughts
Integrating Git and GitHub into your WordPress workflow is one of the easiest ways to improve version control and team collaboration. Whether you’re working on themes, plugins or custom code, this setup keeps everything organized, secure and easy to manage.
With Git, you always know what changed and when. With GitHub, you get cloud backups, transparency and seamless teamwork. Together, they create a smooth, reliable workflow that helps you ship updates faster and avoid costly mistakes.
If you want to streamline development and work more confidently, GitHub + WordPress is the perfect combination.
Ready to build smarter and collaborate better? Start with Bluehost today.
FAQs
Yes, Using Git with WordPress on a live site is possible, but it’s generally not recommended without a local environment. While you can directly push changes to your live WordPress site via GitHub, using a local environment provides safety for testing. WordPress with GitHub or GitHub for WordPress can sync code changes from your local repository to your live site smoothly, ensuring no disruptions.
The primary advantage of using GitHub with Git is version control and easy collaboration. GitHub for WordPress allows developers to track changes, roll back versions and share code easily. Whether you’re working solo or collaborating, WordPress GitHub integration ensures code is securely stored, enabling you to access, update and deploy code from anywhere.
Some of the top GitHub plugins for WordPress include GitHub Embed, WordPress GitHub Sync and Git Updater. These plugins integrate seamlessly with WordPress GitHub integration, allowing you to sync themes, plugins and code changes directly from your GitHub repository to your WordPress site.
To create a WordPress repository on GitHub, sign in to your account and click the “New” button. Give your repository a name, such as “WordPress-Theme” or “WordPress-Plugin,” choose whether it should be public or private and optionally initialize it with a README file. Once the repository is created, you can connect it to your local WordPress theme or plugin folder using GitHub for WordPress or by running Git commands like git init and git push to manage and sync your code.
This setup enables version control and smooth integration with your WordPress projects.
To sync changes between WordPress and GitHub, initialize a Git repository in your WordPress files and push updates using git commit and git push. Whenever you make changes, commit and push them to keep your GitHub repository updated. For deployment, pull changes from GitHub or use tools like WP Pusher to sync themes or plugins to your live site. This keeps your local and live WordPress environments consistently aligned.
Yes, GitHub for WordPress is a powerful tool for version control and collaboration. Whether you’re working on themes, plugins or the entire WordPress site, WordPress GitHub integration allows you to manage your codebase, track changes and collaborate with other developers. You can use GitHub to WordPress workflows to push updates, manage revisions and deploy code directly from GitHub to your live site.
While you cannot host a full WordPress site on GitHub for WordPress directly, you can use GitHub Pages to host static websites. For dynamic WordPress sites, GitHub is used for version control, plugin and theme management. With WordPress GitHub integration, you can manage your codebase and deploy changes easily to your live site, but for the full WordPress setup, you’ll need a traditional hosting provider.
To deploy WordPress to GitHub, initialize a Git repository in your local WordPress folder and connect it to a new GitHub repository using git remote add origin. Push your files with git push -u origin main. Then use WordPress GitHub integration either manually or with plugins like WP Pusher to deploy updates and keep your GitHub and WordPress site in sync.
Yes, there are important security considerations when using GitHub with WordPress. Avoid committing sensitive data like API keys and use .gitignore to exclude critical files. Set proper collaborator permissions and ensure regular code reviews to prevent vulnerabilities. Always use HTTPS and avoid insecure networks. Following these practices helps maintain a secure WordPress GitHub integration.
Yes. GitHub Actions can run CI/CD workflows that SFTP or SSH into your Bluehost server and deploy updated files automatically.
No. Git only tracks files, not databases. You must export/import the database separately when syncing environments.
Not recommended. Track themes/plugins only, not core or uploads.
No. Alternatives include WP-CLI, GitHub Actions, DeployHQ, Buddy CI or manual SFTP.



Write A Comment