Key highlights
- Understand the purpose of the index.html file and its role as your website’s default page.
- Learn when to remove or change index.html, especially during site migration or redesign.
- Discover how to redirect index.html to root or another page using the .htaccess file.
- Fix common issues like WordPress showing the wrong homepage or duplicate index URLs.
- Explore simple troubleshooting steps to handle blank screens or redirect errors effectively.
Ever opened your website only to see an outdated landing page or worse, a blank screen? That’s your index.html file at work. It’s the first file your web server loads and defines what visitors see when they type in your domain name.
But as your site evolves, whether you migrate to WordPress, redesign your homepage or fix duplicate URLs, you may need to change index.html. Or replace it with a new default page.
This guide explains exactly when and how to modify your index.html file safely. You’ll learn how to access your .htaccess, redirect outdated homepages and fix WordPress display issues all using your Bluehost File Manager.
TL;DR: How to change index.html file?
- The index.html is the first file your web server loads as the homepage of your HTML pages.
- To update your first file, open your File Manager in Bluehost and locate the index.html file inside the /public_html/ directory.
- Edit, rename or replace it with a new file (like home.html or index.php) to refresh your homepage content.
- Use .htaccess code to redirect old HTML files or fix duplicate URLs such as /index.html.
- Check that your CSS, header and footer elements display correctly across browsers.
- Always create a backup, test redirects and protect your root directory with a strong password for added security.
What is index.html?
index.html is the default page most web servers load when a visitor accesses a directory (for example, your domain root). If multiple default pages exist, server rules determine the priority.
When to remove or change index.html?
You can change or remove index.html from URL when:
- Migrating from another host with a different homepage name
- Replacing a static HTML homepage with a dynamic WordPress design
- Removing index.html duplicate homepage URLs
- Redirecting old index.html to a new homepage
Let’s explore each of them in more detail:
1. Migrating from another host with a different homepage name
When you move your website from another hosting provider, the previous server may have used a different default document. For example, home.html or default.htm. Your new Bluehost server will still look for index.html first. Updating or renaming the file ensures your site displays the correct default web page instead of showing a blank or outdated screen.
2. Replacing a static HTML homepage with a dynamic WordPress design
Installing WordPress creates a new homepage file, typically index.php. If an older index.html file remains in the same directory, your web server will prioritize it and prevent your WordPress site from loading properly. To fix this, delete or rename the HTML file so visitors see your dynamic WordPress homepage, not an outdated static page.
3. Removing index.html duplicate homepage URLs
Search engines often treat [domain].[com] and [domain].[com]/index.html as two separate URLs. It can cause duplicate content issues and diluted SEO rankings. To prevent this, you can redirect index.html to root using your .htaccess file. This ensures all traffic and link equity point to your main domain (https://[yourdomain].[com]).
4. Redirecting old index.html to a new homepage
If your website’s main page has changed (for example, from index.html to home.html), set up a 301 redirect from the old index file to the new file. This preserves SEO value, helps users reach the updated content and prevents “404 Not Found” errors.
Helpful tip: Always create a backup of your .htaccess and index.html files before making changes. This ensures you can restore your website quickly if something goes wrong during updates or redirects.
Important safety notes before you edit your .htaccess file
Editing your .htaccess file controls how your homepage loads, how redirects work and how your server handles default files. A small mistake can trigger a 500 error, so review these quick safety checks before making any changes:
1) .htaccess works only on Apache servers
Bluehost uses Apache on most Linux hosting plans, so these rules work here. If your site is on a different server type, .htaccess may not apply.
2) Always create a backup first
Download a copy of your .htaccess before editing. This lets you restore your site instantly if something breaks.
3) Linux hosting is case-sensitive
index.html, Index.html and INDEX.html are all treated as different files. Use lowercase names to avoid conflicts.
4) Keep only one default file per directory
Multiple index files (index.html + index.php) can confuse the server and load the wrong homepage.
5) Use these safe, stable rules
These basic examples work for most users and prevent common redirect issues:
a. Set homepage priority
DirectoryIndex index.php index.htmlb. Redirect /index.html to your main domain
Redirect 301 /index.html https://[yourdomain].[com]/6) Avoid syntax errors
Place rewrite rules inside a safety check to prevent 500 errors if mod_rewrite is not active:
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
</IfModule>7) Test after saving
Clear browser, WordPress and CDN cache (if any). Then visit:
https://[yourdomain].[com]/index.html
It should redirect correctly
How to access and edit the .htaccess file in Bluehost Account Manager?
Important: Before adding or changing any .htaccess rule, download a backup of the file first. A small syntax error like a missing space or character can cause a 500 Internal Server Error and break your entire site. Keeping a backup lets you restore your site instantly.
To remove or change index.html file, here is how you can access .htaccess file in Bluehost:
- Log in to your Bluehost Account Manager.
- Click the ‘Hosting’ tab from the side navigation bar to the left.
3. On the main page, click on ‘File Manager’.
4. Look for the ‘Settings’ button, located towards the upper right corner of your screen.
5. From here, click the ‘Preferences’ pop-up, then toggle the radio button for ‘Show Hidden Files (dotfiles)’.
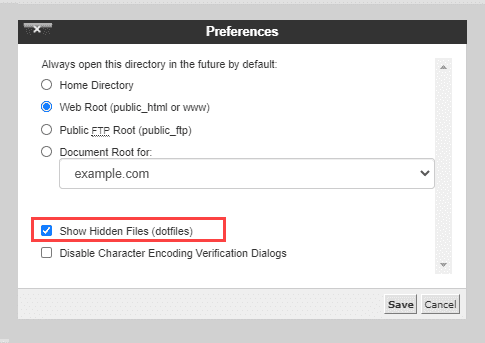
6. Scroll to find the ‘public_html’ from the list, and open it.
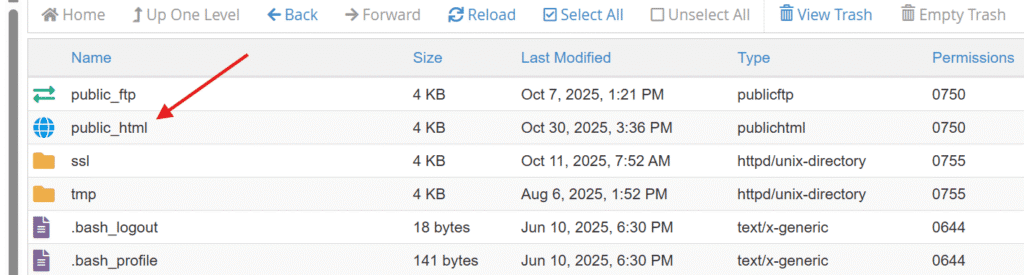
- On the next page, you’ll find .htaccess file.
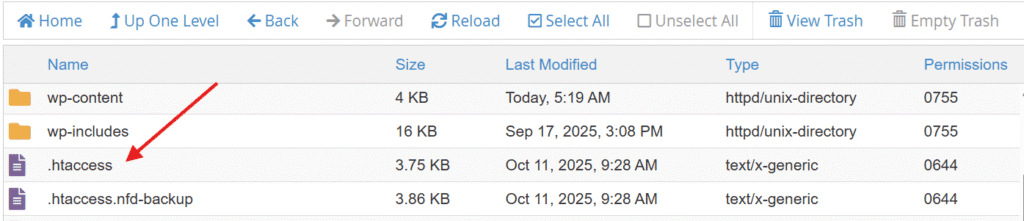
7. Right-click on the file and select ‘Edit’ from the menu.
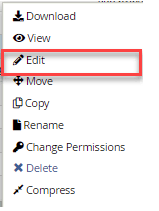
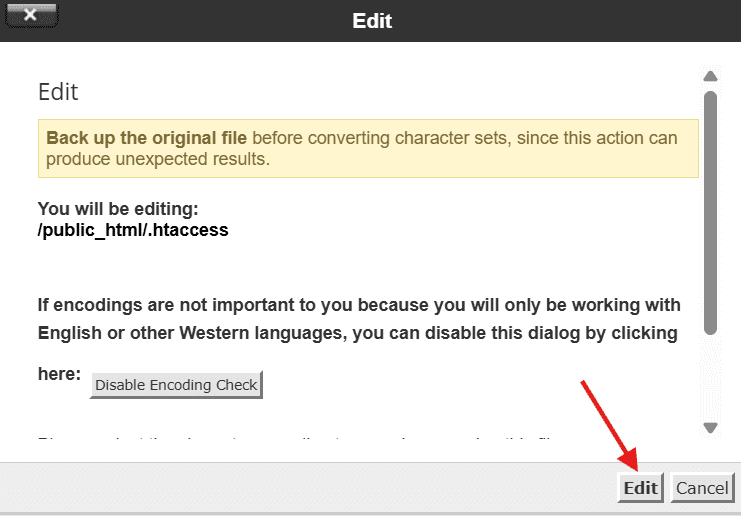
9. There may be a dialogue box asking you about encoding. To proceed, just click on the ‘Edit’ button. The editor will open in a new tab.
How to set a custom homepage using directory index file?
You must modify the directory index file in the .htaccess file. Just insert one of the following codes to the file to accomplish this:
- Making use of Home.htm:
DirectoryIndex home.htm index3.php index.htm index.html default.htm- Making use of Welcome.html:
DirectoryIndex Welcome.html index.htm index.html default.html- Making use of Index.html:
DirectoryIndex Index.html home.htm index.htm index.html default.htmTo learn more about .htacess file, refer to our article: .htaccess Tutorial
How to redirect index.html to root or another page?
If you’ve replaced your old homepage or migrated to a new platform, it’s important to redirect index.html to another page or your root domain. This ensures visitors and search engines always reach the correct default page without encountering broken links or outdated content.
1. Use the .htaccess file for redirection
The simplest and most reliable way to redirect index.html is by editing the .htaccess file in your root directory. This file controls how your web server handles URLs and redirects.
To set a 301 permanent redirect from your old index file to the root domain, follow these steps:
a. Open ‘File Manager’ from your Bluehost Account Manager.
b. Locate and right-click the .htaccess file in the /public_html/ folder.
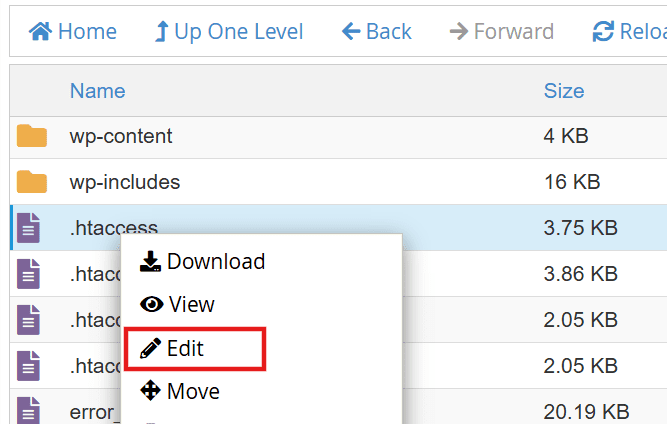
c. Choose ‘Edit’ and paste the following line of code at the top:
Redirect 301 /index.html https://[yourdomain].[com]/This tells the server to forward any request for index.html to your website’s main URL.
2. Redirect index.html to another page
If your homepage has moved to a different file or subfolder (for example, home.html or welcome.php), you can write the address like this:
Redirect 301 /index.html https://[yourdomain].[com]/home.htmlThis redirects index.html to another page, ensuring users automatically land on your new home page or preferred default document.
Not comfortable editing .htaccess? Selected Bluehost web hosting plans also allow you to create 301 redirects from Domains → Redirects inside your Account Manager. This gives you a simple, UI-based way to redirect /index.html without modifying your .htaccess file.
3. Clear cache and test your redirect
After saving your .htaccess file, clear your browser cache or perform a hard refresh (Ctrl + F5).
You can also verify the redirect by visiting this path:
https://[yourdomain].[com]/index.htmlIf the redirect is set correctly, it should take you to your root domain or the new file/page you specified.
Note: Use online tools like httpstatus.io or Redirect Checker to confirm that your 301 redirect is active and points to the correct URL. Always back up your .htaccess before editing to avoid configuration errors.
How to fix WordPress sites showing index.html instead of homepage?
This usually happens when leftover HTML files from a previous site remain in your root directory and override your new setup. You can easily fix this issue directly from your File Manager or via FTP access. Here’s how:
1. Check if index.html is left over from an old site
Open your File Manager and look inside the /public_html/ folder (your site’s root directory). If you see an old index.html file in addition to your new WordPress files (like index.php, wp-config.php or the /wp-content/ folder), that’s likely causing the conflict.
2. Rename or delete the index html file name
To resolve the issue, rename or delete the outdated HTML file. Right-click the file → select Rename and change it to something like index-old.html. This prevents the web server from loading it as the default page while keeping a backup in case you need to restore it later.
3. Verify your WordPress homepage settings
a. In your WordPress dashboard, go to Settings → Reading.
b. In ‘Your homepage displays’, make sure your homepage is correctly set to either ‘Your latest posts’ or ‘A static page’ (depending on your site design).
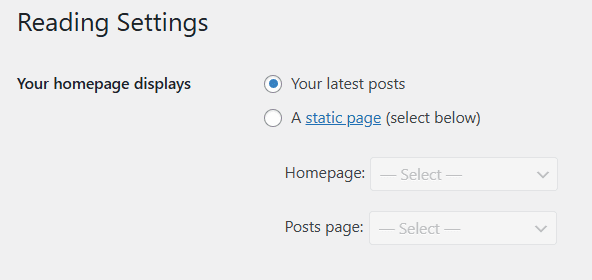
This ensures that WordPress directs traffic to the intended default web page.
4. Clear cache and verify on live site
After editing files, clear both your browser cache and any WordPress caching plugins you’re using. Then, visit your domain URL. It should now display your WordPress homepage instead of the old HTML version.
Tip: If you’re using a CDN like Cloudflare, remember to purge its cache after making file changes. Cached versions of your WordPress index.html file can delay updates from appearing on your live webpage.
Best practices for managing your homepage file
You can manage your homepage file effectively by following these essential best practices:
- Always back up your .htaccess before configuring any settings
- Keep only one index file per directory to avoid conflicts
- Use descriptive homepage names for custom designs
- Test redirects and displays across multiple browsers
- Prevent directory listing for improved site security
Let’s explore each of them in more detail:
1. Always back up .htaccess before editing
Before you modify any setting related to the index.html file or redirect, create a backup of your .htaccess. This small text file controls vital server configurations. Keeping a copy ensures you can restore your site quickly if an edit breaks a web page or causes an unwanted redirect loop.
2. Keep only one index file per directory
Each directory on your web server should contain only one index file like index.html or index.php. Having multiple default pages in the same directory can confuse your server, which may load the wrong default web page or display a blank screen.
3. Use descriptive homepage names for custom designs
If you create a custom HTML file (for example, home.html or landing.html), make sure the file name follows a clear naming convention and is declared properly in your .htaccess under DirectoryIndex. This improves readability and keeps your project structure organized.
4. Test your redirects in multiple browsers
After editing your .htaccess or homepage file, test it in different browsers and devices. This ensures your webpage displays correctly and that images, CSS and JavaScript files load as expected. If you notice outdated content, try clearing your browser cache or perform a hard refresh to load the most recent version of your default page.
5. Prevent directory listing for security
If a WordPress index.html file isn’t present, some web servers automatically display all the files in that folder. This exposes private data or configuration files. To prevent this, always keep a proper default document in place or disable directory browsing through .htaccess by adding:
Options -IndexesThis small line of code helps secure your root directory and other files or folders from unwanted access.
Troubleshooting common issues when you change index.html file
Even small errors in your index.html file or .htaccess configuration can cause your homepage to display incorrectly. Here are the most common issues users encounter, and how to fix them safely using your File Manager or WordPress dashboard.
1. “My homepage is blank or not loading”
This often happens when your web server can’t find the correct default page in the root directory.
- Open your /public_html/ folder and check if your index.html file or index.php exists.
- If it’s missing, upload a new HTML file or create one using File Manager.
- Verify that your file is named correctly. index.html must be lowercase and located in the main directory for most web servers to recognize it.
2. “My WordPress site still shows an old page”
If your WordPress index.html or an outdated file remains in the same directory as your new WordPress setup, it can override your homepage.
- Rename or delete the old file (for example, index-old.html).
- In WordPress, navigate to Settings → Reading and ensure your homepage is set correctly.
- Clear any browser or WordPress cache to see your latest design.
3. “My redirect isn’t working”
If your redirect index.html to root code in .htaccess doesn’t seem to work:
- Make sure the syntax is correct (use Redirect 301 /index.html https://[yourdomain].[com]/).
- Confirm that your server supports .htaccess overrides and that mod_rewrite is enabled.
- If you’ve recently switched domains, check that your new URL is correct and begins with https://.
- Finally, clear your browser cache and CDN cache (if using services like Cloudflare).
4. “Page shows directory listing instead of my homepage”
This happens when no default document (like index.html) is found in a directory. To fix it:
- Upload a fresh index.html file to the folder.
- Or disable directory browsing by adding this line to your .htaccess:
Options -IndexesThis prevents your server from displaying your folder contents publicly.
Tip: If you’re unsure whether your .htaccess edits are applied, download the file, open it with a text editor and double-check for typos or extra spaces.
If you’re stuck or unsure about any of these steps, contact Bluehost Support. Our team is available 24/7 to help you diagnose issues, review your configuration files and guide you through safe fixes. So, your homepage loads exactly the way you expect. Ready for expert help? Reach out to us anytime.
Final thoughts
Changing or removing your index.html file may sound technical. But with the right steps, it’s straightforward and essential for keeping your website organized and secure. Whether you’re replacing a static page with WordPress or setting up redirects, understanding how your default page works or change index.html helps your site run smoothly and rank better on search engines.
Always remember to:
- Back up your .htaccess and homepage file before editing.
- Keep only one index.html or index.php file per directory.
- Test every redirect to confirm it points to the right URL.
With Bluehost WordPress hosting, you can access File Manager and cPanel setting directly from Account Manager. Plus, you get lightning-fast security with built-in caching, global CDN, enterprise-grade security and expert WordPress support to keep your website online and optimized.
Ready to simplify site management? Get started with Bluehost WordPress hosting today and launch a fast, secure and fully optimized website in minutes.
FAQs
index.html is the default homepage file your web server loads when someone visits your domain. It sits in the root directory (public_html) and displays first unless another default page is prioritized in .htaccess.
Open your Bluehost File Manager or connect via FTP, locate index.html in public_html, right-click and select Edit. If you plan to change redirects, back up your .htaccess first before saving changes.
Yes. Rename the file in File Manager, then update .htaccess using a simple rule like: DirectoryIndex home.html index.php index.html
This ensures the server loads your newly named homepage first.
Create a new file named index.html using any text editor. Add your HTML code, save it, and upload it to public_html. The server will automatically load it as your homepage.
Edit your .htaccess file and prioritize PHP like this: DirectoryIndex index.php index.html
This loads index.php before any HTML fallback.
To remove index.html from URL, you can add a 301 redirect inside your .htaccess file: Redirect 301 /index.html https://[yourdomain].[com]/
This tells your web server to redirect index.html to root, keeping your homepage clean and preventing duplicate URLs. It also helps your HTML pages rank better by consolidating link authority under one main domain.
You can open index.html in two ways. First, double-click the file on your computer to open it in your default browser. Or, open Bluehost File Manager → public_html → select index.html → click View or Edit.
No. .htaccess works only on Apache servers. For Nginx, use the index directive and server block rules. For IIS, edit your web.config. If .htaccess instructions don’t apply, your server likely isn’t using Apache.
Use: DirectoryIndex index.php index.html index.htm
This loads dynamic pages first and keeps HTML fallbacks available.
Place a new .htaccess file inside that folder with: DirectoryIndex landing.html index.php index.html
Place the redirect rule above WordPress rules, redirect only /index.html to /, and clear all caches. When tested, /index.html should 301 directly to the bare domain.
Yes. It prevents duplicate homepage URLs and consolidates link equity under your canonical domain, improving crawl clarity and ranking signals.
Nginx: index index.php index.html; location = /index.html { return 301 /; }
IIS (web.config):
Set <defaultDocument> to your preferred file and add a rewrite rule to redirect /index.html to /.
Often, yes. Many plans let you create redirects in Domains → Redirects inside your Bluehost account. If the option isn’t available, edit .htaccess directly via File Manager.


Write A Comment