Key highlights
- Learn how to check MySQL version using phpMyAdmin, SQL queries, hosting panels and command line tools in minutes.
- Follow simple steps for MySQL check version to verify server performance, compatibility and security before updates.
- Use check MySQL version command line for quick results through standard MySQL commands available in shell or terminal.
- Understand how to check MySQL version in Linux using terminal commands and direct server access to view exact build numbers.
- Find how to check what version of MySQL is installed, so you know when to upgrade, optimize queries or troubleshoot server issues.
If your website suddenly breaks or a plugin fails to install, the first thing you should do is check MySQL version. From WordPress updates to database migrations, knowing your MySQL version helps you avoid compatibility issues, performance slowdowns, and stability problems..
The best part is that checking the MySQL version is easy. You can do it using phpMyAdmin, command line, SQL queries or your hosting panel.
In this guide, you will learn how to check MySQL version step by step and find out. Before we get into the methods, let us quickly understand what MySQL is and why knowing the version matters.
What is MySQL? (Quick overview before you check the MySQL version)
MySQL is a popular open-source database server that stores and manages website data.
Whenever a user logs in, submits a form or views a product, the MySQL database is responsible for saving and retrieving that information.
It is widely used with:
- WordPress
- Magento
- Joomla
- Custom PHP applications
MySQL includes two main components:
- MySQL Server: The engine processing queries and managing data
- MySQL Client or command line client: Tools you use to interact with the server
Most users need to check MySQL or view their MySQL version number during tasks like:
- Installing plugins or themes
- Migrating a website
- Troubleshooting database errors
- Improving performance or security
MySQL Database vs MySQL Server Version
| Feature | MySQL Database | MySQL Server Version |
| What it is | Your data (tables, records, content) | The software that processes database requests |
| Why it matters | Stores valuable information | Determines speed, security & compatibility |
| How to check it | View inside phpMyAdmin or Workbench | Run a SELECT VERSION query or version command |
Understanding MySQL release tracks (Updated 2025)
MySQL now follows a dual-track release model that gives users flexibility based on their needs:
Innovation Track vs LTS Track
Innovation Track (9.x series)
- Best for: Developers and teams in fast-paced environments who want cutting-edge features
- Release schedule: New releases every quarter (approximately every 3 months)
- What you get: Latest features, improvements, deprecations, removals and all bug fixes
- Support: Each Innovation release is supported until the next Innovation release
- Current version: MySQL 9.1 (as of December 2024)
- Examples: 9.0, 9.1, 9.2, 9.3, etc.
LTS (Long-Term Support) Track
- Best for: Production environments requiring stability and minimal behavior changes
- Release schedule: New major LTS release approximately every 2 years
- What you get: Only critical bug fixes and security patches—no new features after the first LTS version
- Support: 5 years of premier support + 3 years of extended support (following Oracle Lifetime Support Policy)
- Current LTS version: MySQL 8.4.x series
- Key benefit: In-place upgrades and downgrades are possible within the same LTS series (e.g., from 8.4.0 to 8.4.3 and back)
Which track should you choose?
Choose Innovation Track (9.x) if:
- You’re developing new applications and want the latest features
- Your team has robust automated testing and CI/CD pipelines
- You can commit to quarterly updates
- You prioritize new capabilities over long-term stability
Choose LTS Track (8.4.x) if:
- You’re running production websites or critical applications
- You need predictable behavior with minimal changes
- You want longer support cycles without frequent upgrades
- Stability and compatibility are your top priorities
- You’re migrating from MySQL 8.0.x
Why checking your MySQL version matters more than ever
With the new release model, knowing your exact MySQL version helps you:
- Determine your upgrade path: Innovation and LTS tracks have different upgrade requirements
- Plan maintenance windows: Innovation requires quarterly updates; LTS needs less frequent updates
- Ensure compatibility: Features available in Innovation may not exist in LTS versions
- Optimize performance: Each track has different performance characteristics and optimizations
- Maintain security: Both tracks receive security patches, but on different schedules
Current MySQL versions (December 2025)
- Innovation Track: MySQL 9.1.x (latest features)
- LTS Track: MySQL 8.4.3 (stable, production-ready)
- Legacy Bugfix Track: MySQL 8.0.39 (security patches only, migrate to 8.4.x recommended)
Important note: MySQL 8.0.x is in bugfix-only mode. Users are encouraged to migrate to MySQL 8.4.x LTS for continued feature support and longer lifecycle.
Also read: How to Create and Delete MySQL Databases and Users
How to check MySQL server version — quick answer table
If you want to quickly check the MySQL version, you can find it using phpMyAdmin, the MySQL command line client, SQL queries or system tools like command prompt, terminal or MySQL Workbench.
These methods help you identify your current version, server status, user login details, supported features and more. Here is the fastest way to compare all methods at a glance:
Quick ways to check MySQL version
| Method | Where you run it | What it shows | Best for |
| phpMyAdmin interface | Web hosting panel like cPanel | Shows server version on dashboard home screen | Beginners / Shared hosting |
| MySQL -V command | Terminal or command prompt | Displays client build and version number | Linux & Windows users |
| SELECT VERSION(); query | MySQL client / MySQL Workbench | Returns current MySQL version output | Developers or DB Admins |
| SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘version’; | SQL console or CLI | Shows server variables including MySQL version number | Detailed configuration checks |
| MySQLadmin version | Command line client | Displays admin info & server status | Administrative operations |
| SSH shell | Remote access terminal | Checks if local MySQL server responds securely | Advanced users / Server-level testing |
Important note: As of 2025, the recommended MySQL versions are MySQL 8.4.x LTS for production environments and MySQL 9.x for development with cutting-edge features. MySQL 5.7 reached End-of-Life in October 2023 and MySQL 8.0.x will reach EOL in April 2026.
These commands allow you to easily check version details, compare builds, verify installation and confirm MySQL is running. In the next section, we’ll walk through each method step-by-step so you can execute the correct syntax based on your device and environment.
What are the different methods to check MySQL version?
You can check the MySQL version in multiple ways depending on your access level, operating system and workflow. Some users prefer a phpMyAdmin interface, while others use the MySQL command line client, MySQL Workbench or SSH connection on a remote server.
Here are the most common ways to view your MySQL version number:
GUI (Graphical Interface) methods
Best for beginners or hosting users
- Check version using phpMyAdmin
- View version through MySQL Workbench
- Hosting dashboards like cPanel or Plesk
Command line methods
Best for developers, Linux users or server admins
- Run SELECT VERSION(); query
- Use MySQL -V or MySQLadmin version
- Execute SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘version’; for detailed configuration
- Check via SSH shell (secure, encrypted connection)
System + Network Level Checks
For advanced debugging and server status verification
- SSH connection to confirm local MySQL server availability (secure method)
- Verify server status, output logs, variables and installation build
Each method returns relevant information about the version of MySQL installed, along with other details like user access, server variables, configuration and software build.
Now let’s break down each method with short steps and commands so you can easily check what you are running.
1. How to check MySQL version in phpMyAdmin
If you prefer a visual interface, the easiest way to check the MySQL version is through phpMyAdmin. Most hosting providers, including cPanel-based plans, offer phpMyAdmin by default, so beginners and Windows users find this method simple and quick.
Steps to find MySQL version using phpMyAdmin interface
Step 1: Log in to your hosting control panel and click on cPanel, Plesk or similar.
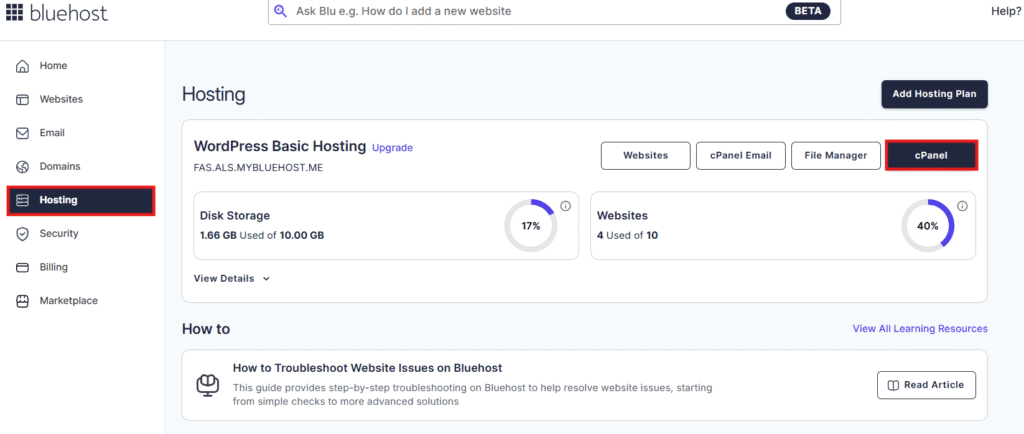
Step 2: Open phpMyAdmin under the database tools section.
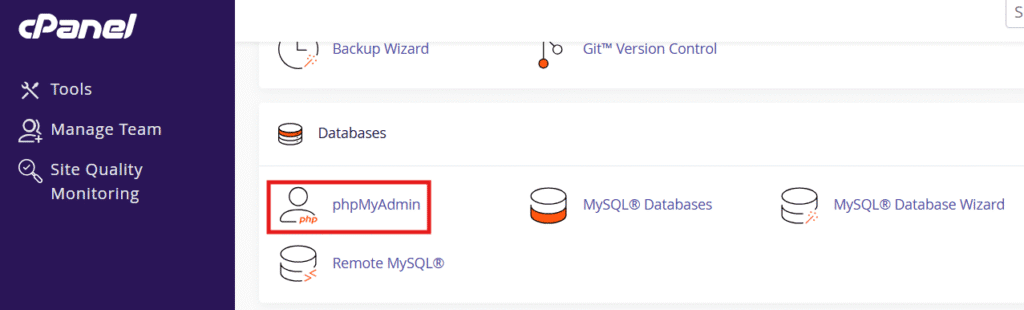
Step 3: Look for the server version number displayed on the home screen.

Step 4: You will also see database server information, MySQL client build and server status.
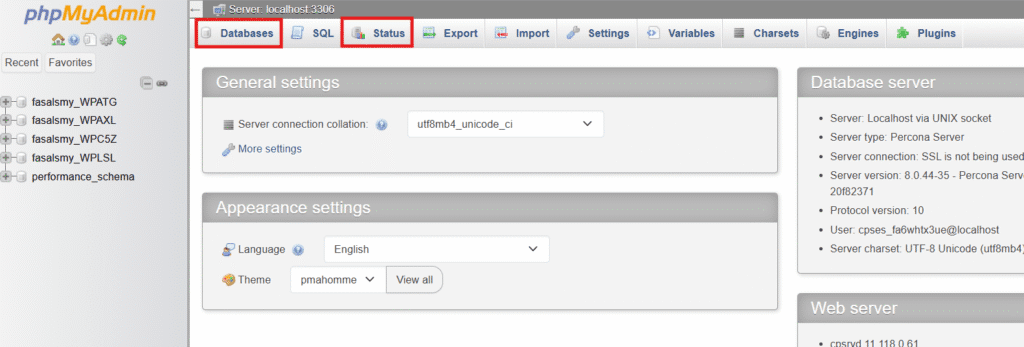
You can usually find version details in the top-right or center panel. It may appear as:
MySQL version: 8.4.x or 8.0.xx
This shows the current version, build type and sometimes release notes.
When to use this method
- You do not want to use command line or SSH
- You only need quick MySQL version information
- You are checking a shared or hosted environment
- You want details like username, variables, logs and access permissions at a glance
phpMyAdmin also supports SQL queries, so if needed, you can easily run:
sql
SELECT VERSION();sql
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'version'; This gives a deeper breakdown of version details, configuration variables and server information.
2. Check MySQL version command line (MySQL CLI/SSH)
If you are comfortable using terminal or CMD, the MySQL command line client is the fastest way to check the MySQL version number. This method works on Linux, macOS and Windows systems and is ideal for developers or users with SSH access to a server.
Method 1 – Using MySQL -V (Quick check)
This is the simplest command to run and does not require login.
Open command prompt / terminal and type:
bash
MySQL -V Output example:
MySQL Ver 8.4.3 for Linux on x86_64 This displays the version of MySQL client installed on your system.
Windows users: If the command doesn’t work, you may need to navigate to the MySQL bin directory first:
cmd
cd "C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.4\bin"
MySQL -V Or add MySQL to your Windows PATH environment variable for permanent access.
Method 2 – Log in to MySQL shell
Use this if you want deeper details about the server version and configuration.
Run the following command:
bash
MySQL -u root -p Enter your MySQL username and password, then execute:
sql
SELECT VERSION(); Expected output example:
8.4.3 This shows the current MySQL version running on your server.
Method 3 – Show version variables
If you want configuration-level information, use:
sql
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'version';This returns:
- Server version
- MySQLadmin version info
- Variable build metadata
- Relevant version information for upgrades
Bonus Method – Use STATUS command
For comprehensive server information including version, uptime and connection details:
sql
STATUS; This displays version along with server statistics in one command.
When should you use command line?
| Use CLI if you need | Why |
| Faster version lookup | One command, instant result |
| Server-level details | Useful for upgrades or troubleshooting |
| SSH shell access | Remote system checks & logs (secure encrypted connection) |
| Advanced administrative operations | Run SHOW VARIABLES, validate server status |
This method is best for power users, database admins and anyone managing a remote or local MySQL server.
3. How to check what version of MySQL is installed using SQL queries
If you are already inside the MySQL shell or working through tools like MySQL Workbench, you can easily check the version using SQL statements. This method is highly reliable because it reads the version directly from the database server.
Method 1 – Use SELECT VERSION();
This is the most common and direct query.
sql
SELECT VERSION();Output example:
8.4.3 This displays the current version of MySQL installed on your server.
Method 2 – Show detailed version variables
If you want configuration-level information instead of just a simple number, use:
sql
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'version'; This query returns:
- MySQL version number
- Build details
- Release information
- Other server variables related to versioning
Method 3 – Check version, server status and administrative info
You can also use:
bash
MySQLadmin version
This command shows:
- Server status
- Uptime
- Log-level details
- Administrative operations info
Ideal for users managing a remote or local MySQL server.
When is this method best?
| Best for | Why |
| Developers and DB administrators | Clean SQL-based output |
| Checking configuration variables | Queries show deep server details |
| Workbench / GUI users | Run queries with one click |
| Cross-platform use (Linux, macOS, Windows) | SQL works everywhere |
SQL queries are simple, fast and return relevant information, making them one of the best ways to verify your current MySQL version.
4. How to check MySQL version in WordPress dashboard
If you manage a WordPress site, you can check the MySQL version without using terminal or commands. WordPress provides built-in tools that show database details, including the MySQL version number, server information and environment configuration.
This method requires no command line usage, so it’s ideal for beginners, bloggers, small business owners and non-technical users.
Method – Check MySQL version using WordPress Site Health tool (Built-in)
WordPress has included the Site Health feature since version 5.2 (2019), so you don’t need any additional plugins.
Follow these steps:
Step 1: Log in to your WordPress wp-admin dashboard
Step 2: Go to ‘Tools’ and click on ‘Site Health’.
Step 3: Open the ‘Info’ tab.
Step 4: Scroll down to the ‘Database’ section.
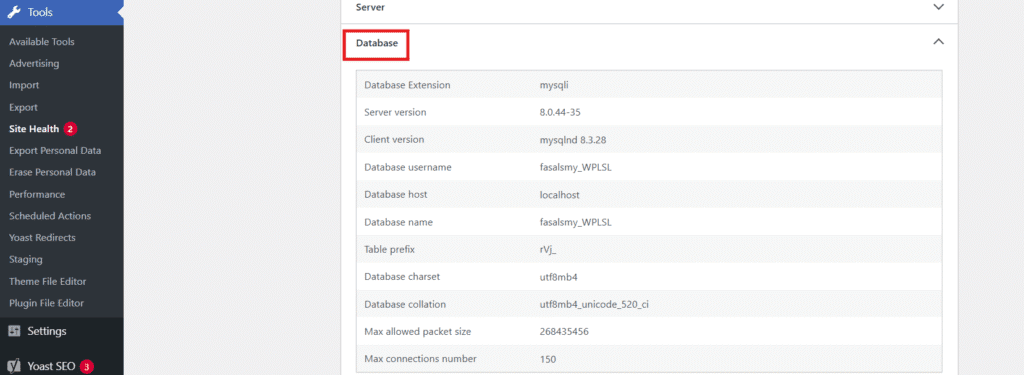
Step 5: Look for MySQL version information.
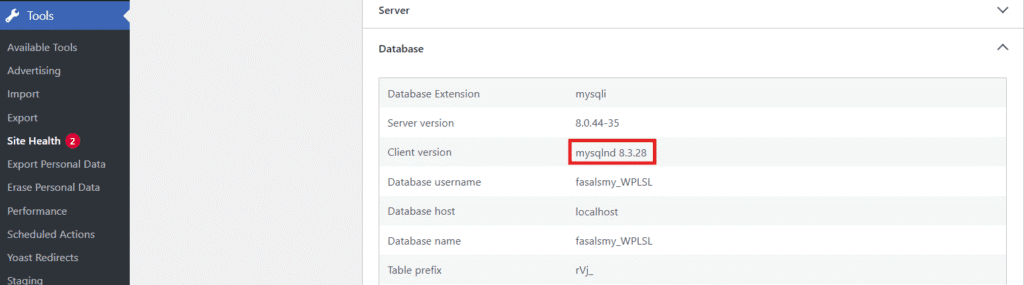
You’ll see something like:
Database server: MySQL 8.3.28.This shows your current version, database engine and related server variables.
Optional – Use a WordPress plugin (for advanced details)
If you prefer additional insights or visual breakdown, plugins like:
- Query Monitor (shows database queries and performance)
- Health Check & Troubleshooting (extended diagnostics)
- WP System Health (enhanced system information)
can show MySQL server status, PHP version and system configuration in more detail.
Note: Most users don’t need plugins for basic version checking—the built-in Site Health tool is sufficient.
When is this method ideal?
| Use case | Benefit |
| Don’t want to run commands | No terminal or MySQL Shell required |
| Want quick MySQL version lookup | 30-second check inside dashboard |
| Manage multiple websites | Fast visibility for server status |
| Are not comfortable with SSH or command prompt | Beginner-friendly method |
This is one of the easiest ways to check what version of MySQL is installed when you only have access to WordPress.
5. How to verify MySQL server connectivity (Advanced troubleshooting)
If you want to verify whether your database server is responding, you can check MySQL server connectivity to confirm the service is running and accessible over the network.
This is useful when you are troubleshooting remote access issues or checking connectivity between applications and the database server.
Method – Connect using SSH (Recommended secure method)
The secure way to test connectivity is using SSH:
bash
ssh user@your-server-address
MySQL -u root -p This confirms MySQL is accessible and allows you to run queries securely.
Alternative – Testing port connectivity (Advanced)
To test if MySQL port 3306 is open and responding:
bash
telnet your-server-address 3306 Or using a more modern tool:
bash
nc -zv your-server-address 3306 Important Security Notes:
- Telnet is unencrypted and deprecated for security reasons
- Most modern hosting environments block Telnet by default
- Always use SSH for remote server access instead
- This method primarily confirms connectivity, but may not reliably display the version number due to security configurations
When should you use connectivity testing?
| Use case | Why this method helps |
| MySQL is not responding or failing to connect | Verifies if the port is open |
| Checking server-level availability | Confirms MySQL is running before login |
| Firewall or network debugging | Tests if MySQL port is accessible |
| Remote server troubleshooting | Validates connection path |
Recommendation: Use SSH for secure remote access and run SELECT VERSION(); once connected for accurate version information.
6. How to check MySQL version in Linux / cPanel / hosting control panels
If you’re working on a Linux server or using hosting tools like cPanel or Plesk, you can check MySQL version using both interface-based and command-line methods. This is helpful if you’re managing a production site, accessing a database remotely or performing various administrative operations.
Method 1 – Check MySQL server version in Linux (terminal)
Most Linux users prefer the command line because it is fast, clean and direct.
Use the following command to view version details:
bash
MySQL -V This instantly displays the MySQL version number installed on your system.
If you want deeper details, log into the MySQL shell:
bash
MySQL -u root -p Enter your root password and run:
sql
SELECT VERSION(); This query shows the current version, build number and MySQL release.
Method 2 – Check version inside cPanel or Plesk
If you’re using shared hosting, you don’t need terminal access.
Steps:
Step 1: Log into your hosting panel
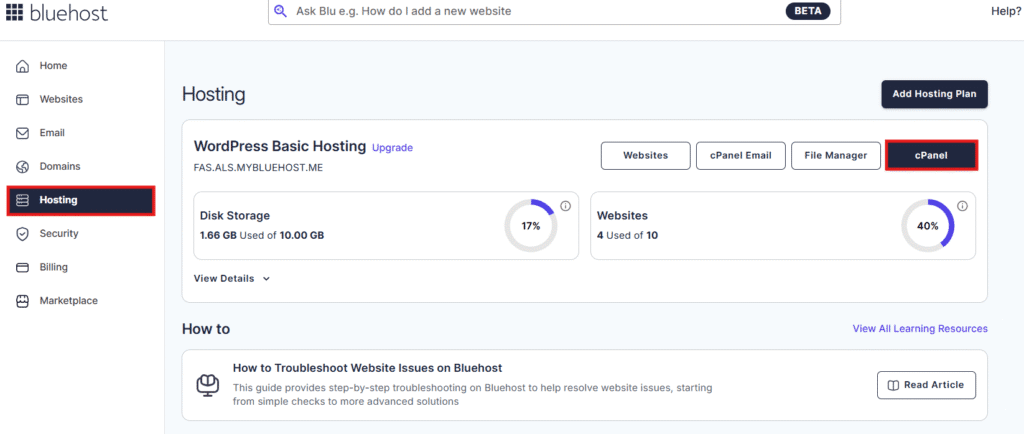
Step 2: Open phpMyAdmin
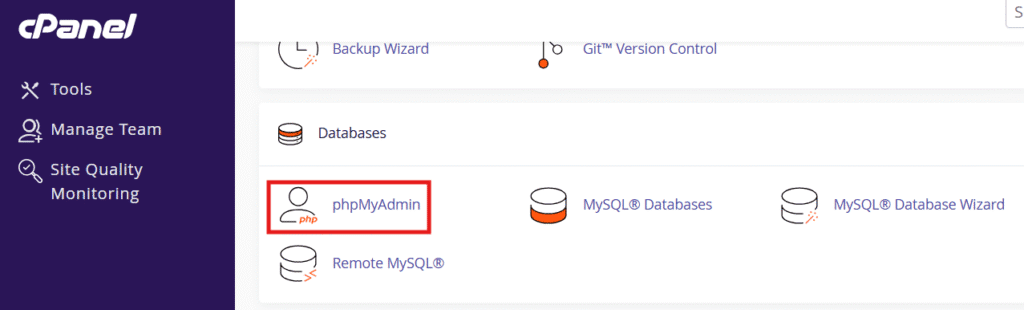
Step 3: Look at the home screen for MySQL server version
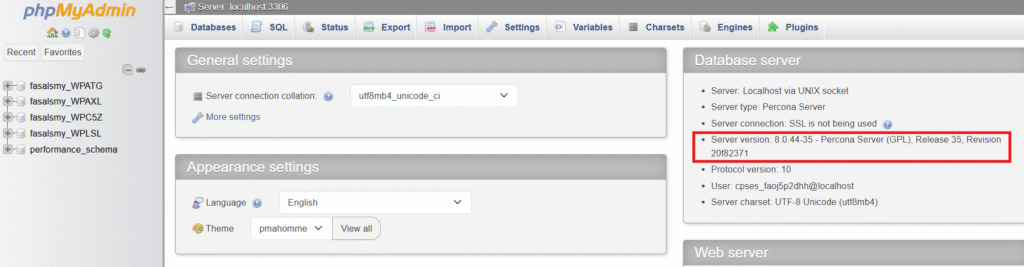
Step 4: You can also scroll to the database server section
This method is beginner-friendly and works without commands.
Method 3 – Check MySQL version through GUI tools
If you prefer graphical tools instead of command line:
- MySQL Workbench
- phpMyAdmin
- Hosting dashboard database viewer
can show version details easily. These tools also allow imports, exports and administrative operations.
When should you use this method?
| Use case | Best option |
| You prefer commands | Use Linux terminal or command prompt |
| You don’t want commands | Use cPanel phpMyAdmin interface |
| You need MySQL configuration details | Use SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘version’ |
| You forgot login credentials | Use hosting access recovery options |
Whether you’re on Linux, cPanel or another hosting panel, you can check the MySQL version without effort.
MySQL version recommendations for 2025
When checking your MySQL version, it’s important to know which versions are currently recommended:
Production environments
- MySQL 8.4.x LTS (Long-Term Support)
- 5 years of premier support + 3 years extended support
- Stable, security-focused, minimal changes
- Best for live websites and critical applications
Development environments
- MySQL 9.x Innovation Track
- Quarterly releases with latest features
- Best for testing new capabilities
- Not recommended for production
Versions to upgrade from
- MySQL 5.7: End-of-Life reached October 2023
- MySQL 8.0.x: EOL scheduled for April 2026
- Users should migrate to MySQL 8.4.x LTS
Knowing your current version helps you plan upgrades, ensure security and maintain compatibility with modern applications.
Why you should check MySQL version?
Knowing your MySQL version is more important than it seems. Whether you manage a WordPress site, run an ecommerce store or handle data-heavy applications, the current MySQL version determines performance, compatibility and security.
Here’s why you should always check the MySQL version before updating software or making system changes:
1. Compatibility with plugins, themes and apps
Certain plugins or CMS tools require a specific MySQL server version. If the version is outdated, features may break or stop working.
2. Security and stability
New releases often include important security fixes. Running the latest MySQL version helps protect your website data and reduce vulnerabilities.
3. Better performance and speed
Updated versions usually come with improved indexing, query handling and storage engines. This helps your website load faster and process requests more efficiently.
4. Troubleshooting and debugging
Version knowledge helps when you execute queries, solve connection errors or use MySQL command line client tools to check logs or server status.
5. Smooth upgrades and migrations
If you plan to upgrade, migrate or move to a new host, checking your version first avoids downtime or configuration conflicts.
In short, knowing your MySQL version information gives you clarity, control and confidence while managing your website or database server.
Understanding MySQL version numbers
Before you upgrade or troubleshoot a database, it helps to understand what the MySQL version number means.
The version format usually looks like this:
8.0.34
5.7.42 Each part has meaning and knowing it helps you determine stability, support and new features available in the build.
MySQL version breakdown
| Segment | Example | Meaning |
| Major version | 8 / 5 | Feature set, architecture changes |
| Minor version | 0 / 7 | Security patches, enhancements |
| Patch version | 34 / 42 | Bug fixes, maintenance updates |
When you check the MySQL version, whether via command line or GUI, this structure will appear in the result or query output.
Why version numbers matter
When you know your current version, you can:
- Identify whether you’re running the best MySQL version or an older build
- Determine what new features you can access after upgrading
- Understand compatibility with WordPress, PHP, themes and extensions
- Perform safer updates with fewer errors or data issues
Different versions may support different syntax or performance improvements, so always check compatibility before you upgrade.
Quick ways to verify version details
Run any of the following commands inside MySQL shell or command prompt:
SELECT VERSION();
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'version'; These statements return the version number, configuration details and relevant information about the server.
Knowing how version numbers work helps you choose the correct update path and avoid conflicts when running scripts or applications.
Should you upgrade MySQL server version?
Checking your MySQL version is the first step.
The next question is whether you should upgrade or continue using your current build.
Upgrading is often beneficial, but the right decision depends on compatibility, stability and server requirements.
When upgrading MySQL makes sense
You should consider upgrading if:
- Your current build is outdated or no longer supported
- You want access to new features, performance boosts and better indexing
- Your CMS or application recommends a newer version of MySQL
- You are experiencing slow queries or server response issues
- You are planning a migration, theme update, plugin installation or system expansion
Newer releases offer security patches, better optimization, improved storage engines and advanced SQL support — all of which help keep your website running efficiently.
When you may wait instead
You may postpone upgrading if:
- You rely on old scripts or legacy applications
- Your system is stable and you do not need new features
- You have compatibility concerns with plugins or code
- You do not have a tested backup or rollback option
Stability is important. A newer version is not always better if your environment isn’t prepared for the change.
Quick decision guide
| Upgrade? | If yes | If no |
| When you need performance & features | Upgrade to supported stable builds | Stay until testing is complete |
| When software requires a specific version | Upgrade after backup | Review compatibility first |
| When debugging, errors or slow queries occur | Update to optimized version | Monitor status before changing |
If you’re unsure, checking server status, compatibility and system logs can help you decide safely.
How to upgrade MySQL version safely?
Upgrading MySQL is not just about clicking update.
It requires preparation, backup and testing to avoid data loss or downtime.
Before you upgrade, always check the MySQL version, verify compatibility and ensure your site or app supports the new release.
Follow these steps for a safe upgrade
- Back up your database
Export all tables, users and configuration settings.
A safe rollback gives you protection if anything fails.
- Check version compatibility
Confirm theme, plugin, CMS and PHP support.
Older tools may not work with the best MySQL version.
- Review release notes
Look for performance changes, deprecated features and syntax updates.
- Test in staging environment (recommended)
Never upgrade live systems without a test run.
- Perform the upgrade
Use hosting panel, terminal or OS package manager.
- Verify installation using the following command:
SELECT VERSION();You should now see the current version updated successfully.
Upgrade paths based on your environment
1. Upgrade MySQL using cPanel
You can upgrade through the hosting dashboard if your provider supports it.
Steps:
- Log in to cPanel
- Open MySQL Database or software management menu
- Select update/MySQL version options
- Confirm and apply upgrade
After upgrading, run SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘version’; to verify.
2. Upgrade MySQL in Linux/Ubuntu
Linux users can upgrade through command line tools.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install MySQL-serverThen check using:
MySQL -V 3. Upgrade MySQL on macOS
If installed via Homebrew:
brew update
brew upgrade MySQL Restart MySQL service afterward and run:
SELECT VERSION();4. Upgrade MySQL in Windows
Windows users can upgrade using MSI packages or MySQL Installer.
Steps:
- Download the latest MySQL installer from the official site
- Launch setup and choose upgrade
- Complete installation and restart services
Verify version from command prompt using:
MySQL -V Final thoughts
Checking your MySQL version is one of the simplest yet most important steps when managing a website or application. It helps you understand what your server supports, which features are available and whether you may need an upgrade for better performance.
You can easily check the version using phpMyAdmin, SQL queries, command line tools or hosting panels depending on whether you prefer a graphical interface or terminal-based workflow.
Once you know your MySQL version number, you can plan updates more confidently, troubleshoot errors faster and avoid compatibility issues with plugins, themes or scripts. Upgrading should always begin with a backup, a quick compatibility check and a safe deployment method.
Bluehost offers optimized servers, one-click tools and 24/7 support for smooth database management. Explore our plans today.
FAQs
You can check the installed MySQL version using phpMyAdmin, SQL queries or command line.
Run MySQL -V for a quick view or log into MySQL shell with MySQL -u root -p and execute:
SELECT VERSION();
This returns the current version along with build details and configuration.
Open command prompt and run any of the following commands:
MySQL -V
MySQL –version
These commands return your MySQL or Oracle-compatible version number instantly.
Login to MySQL shell:
MySQL -u root -p
Then execute:
SELECT VERSION();
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘version’;
You may also use a status command for additional details including uptime and current input statement tracking.
Use this SQL query:
SELECT VERSION(), CURRENT_DATE;
This displays your MySQL server version along with today’s date in a single output so you know exactly when the database was checked and when commands end successfully.
MySQL uses port 3306 by default. Port 1433 belongs to Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle-related environments may use other ports depending on setup.


Write A Comment