Key highlights
- Understand how domain forwarding and masking work so you can choose the right method for your website’s SEO, branding and user experience.
- Learn when to use permanent (301) and temporary (302) redirects to preserve search visibility, link equity and site usability during rebrands or campaigns.
- Explore how domain masking simplifies URLs and maintains brand consistency but can limit SEO performance, analytics accuracy and user trust.
- Know the key differences between forwarding and masking, including their effects on URL visibility, SSL security, analytics and overall transparency.
When you register a domain, you may want it to lead visitors to a different website or display a customized URL in the browser instead. This is where domain forwarding and masking come into play, helping you control how users access and view your website.
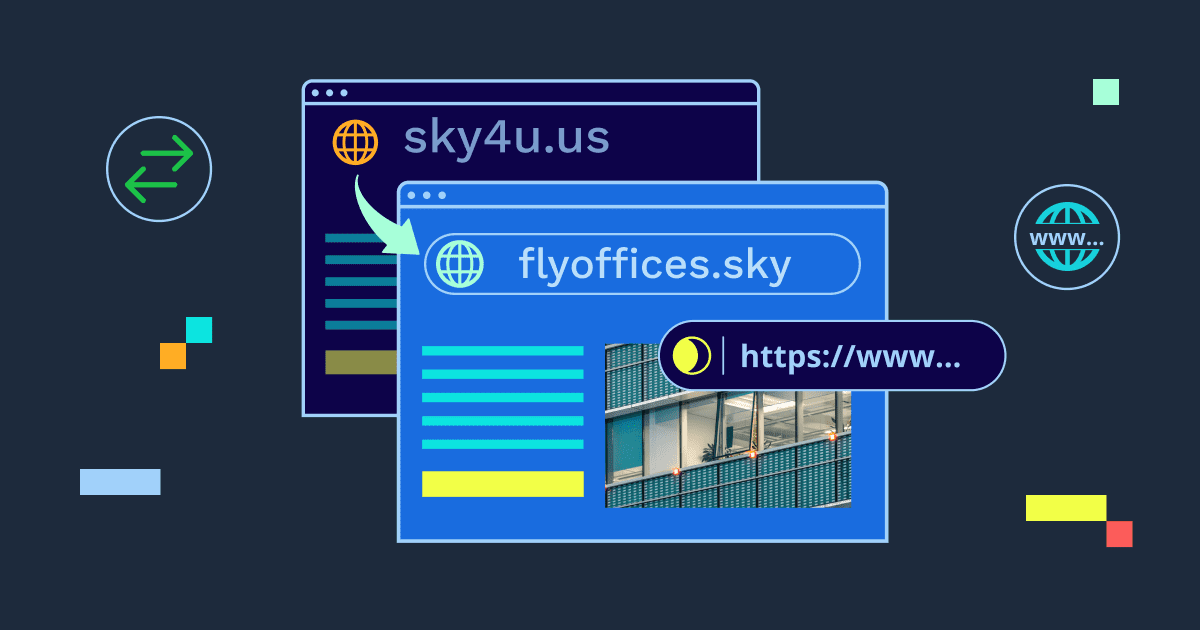
Both techniques help manage how visitors reach and view your site, but they function very differently. Domain forwarding automatically redirects users to another domain, while domain masking hides the original URL and displays a chosen one instead.
Understanding the difference between domain forwarding and masking helps you make informed decisions about SEO, branding and analytics. It also ensures that your visitors enjoy a seamless browsing experience across the internet without confusion or loss of trust.
In this blog, we’ll explain what is domain forwarding with masking, how both processes work and the difference between domain forwarding and redirect, so you can choose the better option for your website.
What is domain forwarding?
Domain forwarding, also known as URL forwarding, is the process of automatically redirecting visitors from one domain to another. When someone types your old or alternate domain into the browser, they’re sent to a new destination URL, usually your main website or landing page.
This is useful when you own multiple domains, are rebranding or want to make sure users find the right website even if they type a misspelled version of your domain. It helps preserve your existing traffic and ensures visitors always land on the correct site.
Domain forwarding tells search engines that one domain permanently points to another, helping preserve your site’s SEO value and visibility.
Let’s look at how domain forwarding works in practice.
How domain forwarding works
When you enable domain forwarding, your registrar or hosting provider automatically redirects visitors to a specific destination URL. This happens at the server level, so users are seamlessly sent to the new location without taking any action.
For example, if someone visits ([yourbrandstore].[net]), you can forward them to [(yourbrandstore].[com]). The browser updates to show the new domain and search engines recognize the correct destination.
The browser updates to show the new domain and search engines recognize the correct destination.
Forwarding and masking may look similar, but forwarding performs an actual redirect, while masking hides the original URL. You can apply forwarding to a single page, a subdomain or an entire website.
It’s commonly used when you own multiple domains, migrate to a new website, consolidate branding or run short-term campaigns. You can choose between temporary (302) and permanent (301) forwarding to control how search engines treat your redirects.
Domain forwarding without masking
Domain forwarding without masking is the standard form of redirect, where the browser shows the final destination URL. This method preserves SEO value, maintains analytics accuracy and provides a clear brand experience.
Key benefits:
- Passes SEO authority with 301 redirects
- Keeps analytics and tracking accurate
- Maintains brand consistency and user trust
- Avoids technical issues associated with masked URLs
This approach is ideal for website migrations, consolidating multiple domains or redirecting typo domains and alternate extensions, ensuring your website’s visibility, authority and user experience remain intact.
Types of domain forwarding
There are two main types of domain forwarding: 301 (permanent redirects) and 302 (temporary redirects). Understanding temporary vs permanent domain forwarding is essential, as each tells search engines how to treat the redirected page and impacts SEO differently.
301 (Permanent redirect)
A 301 redirect tells search engines that a domain or page has permanently moved to a new location. It transfers most of the original page’s SEO value, including backlinks and rankings, to the new domain.
Use this option when:
- You’re rebranding or switching to a new domain.
- You’ve changed your site’s structure or URL format.
- You want to keep existing search visibility and link authority.
Because it passes SEO signals, 301 is the preferred choice for long-term domain changes.
302 (Temporary redirect)
A 302 redirect indicates that the change is temporary. It sends visitors to a new URL without transferring the full SEO value to the destination domain.
Use this option when:
- Your website is under maintenance or redesign.
- You’re running a short-term campaign or event.
- You want to test new pages without affecting SEO rankings.
Since it doesn’t pass SEO equity, 302 is ideal for short-term redirections only.
Also read: How to Redirect a URL (301, 302 & More) – Beginner’s Guide
Choosing the right redirect type depends on your goal, preserving SEO during rebrands or maintaining usability for temporary campaigns.
Next, let’s see when to use domain forwarding for the best results.
When to use domain forwarding
Domain forwarding helps manage multiple domains, protect SEO value and create a consistent online presence. It’s also important to recognize the difference between permanent and temporary domain forwarding when setting up redirects to ensure the right type of redirect aligns with your business needs.
It ensures visitors always reach the correct site, even if they use alternate or outdated domains. Unlike URL masking, forwarding updates the browser address bar to show the original website URL instead of displaying a masked URL.
Here’s when forwarding is most useful.
1. Branding consistency
Forwarding helps unify your brand by directing all domain variations to one main website. Whether users type your .net, .org or .com version, they’ll land on the same homepage. This maintains a professional image and consistent brand identity across all web addresses, including key sections like your contact or about page.
2. Fixing typos and variations
Visitors often make typing errors when entering web addresses. By forwarding typo or alternate versions of your domain to the correct one, you prevent lost traffic and ensure users always reach your intended site. This protects both your credibility and user experience, ensuring visitors are never sent to the wrong or masked URL.
3. Rebranding or migration
When changing your domain name or restructuring your site, a 301 redirect transfers link equity and SEO value to the new domain. It tells search engines the move is permanent, helping maintain rankings and ensuring users seamlessly find your updated website without relying on URL masking or hidden redirects.
4. Marketing campaigns
Forwarding helps you create short, memorable domains for campaigns and promotions. These easy-to-type URLs can redirect users to detailed landing pages, product offers or even your contact page. This helps improve engagement and conversions without changing your main website’s structure.
5. Temporary redirects
If your site is undergoing maintenance or updates, use a 302 redirect to forward visitors temporarily. It keeps your website accessible and avoids broken links, ensuring users still reach a relevant page until your main site is ready to go live again.
What is domain masking?
Domain masking is a technique that hides the actual URL of a website and shows a different domain name in the browser’s address bar. When someone visits a masked domain, the displayed address remains the same even though the content is pulled from another site.
This creates a seamless viewing experience for visitors while maintaining a consistent brand appearance. Website owners often use domain masking to simplify long or complex URLs or to display one brand domain across multiple pages or third-party platforms.
Also read: Domain Masking & URL Cloaking: Pros, Cons and Best Practices
However, masking doesn’t truly redirect traffic, it only overlays content using HTML frames or scripts. While it can make links look cleaner, it doesn’t transfer SEO value and may cause issues with analytics or tracking.
How domain masking works
Domain masking keeps a website’s displayed URL the same while showing content from another domain. When users visit the masked domain, they see one web address in the browser’s bar even though the site’s data is loaded from a different location.
This is usually done through HTML frames, meta refresh tags or settings configured at the domain registrar. The technique helps maintain consistent branding but doesn’t redirect traffic, it simply hides the real source URL from visitors and search engines.
When to use domain masking (and when to avoid it)
Domain masking can be useful in limited situations but isn’t ideal for long-term websites or SEO-focused projects. Below are common instances where it helps and cases where it should be avoided to protect site visibility, analytics accuracy and user trust.
Use domain masking when:
You can use domain masking in selective cases where you want to manage URL redirects without revealing the original destination.
Below are the scenarios where using the masking option can be beneficial:
- You want to hide long or complex URLs: If your original links contain long URLs or tracking parameters, the masking option helps simplify them. Visitors see a clean domain instead of confusing links, making them easier to remember and share in marketing materials or emails. This is especially helpful when you don’t want to expose redirects or meta tags from a different website.
- You want to maintain brand consistency for a simple site: Masking allows you to display one branded domain across all pages, even if they point to a different website. This ensures brand consistency without URL redirects or restructuring your hosting setup, ideal for microsites or event pages meant for general site visitors.
- You’re running short-term promotions: For time-bound offers, affiliate campaigns or temporary landing pages, domain masking provides quick setup and user-friendly URLs. It keeps your brand name visible during short-term promotions, giving visitors a cohesive, branded experience without noticing the hidden source.
- For temporary landing pages: If you’ve created a quick landing page using a third-party builder, masking lets you display your main domain to reinforce brand credibility. It’s generally suitable for limited campaigns where both SEO performance and keyword optimization aren’t the primary goals.
Avoid domain masking when:
While domain masking can make links look cleaner, it comes with trade-offs that can affect your site’s long-term growth and trustworthiness.
Below are key scenarios where using proper URL redirects or standard forwarding is the better choice:
- SEO performance is a priority: Masking prevents search engines from indexing the real website content. Since the masked domain doesn’t use proper URL redirects, it blocks SEO signals and reduces ranking potential for your target keywords. If you rely on both SEO and paid campaigns, replace domain masking with standard forwarding for better performance.
- You rely on accurate analytics: Because masking hides the true URL, it interferes with tools like Google Analytics or other traffic trackers. This makes it difficult to measure user clicks, engagement or conversions accurately, leading to poor insights about your site visitors.
- Transparency and trust matter to your users: When website visitors notice a mismatch between the visible domain and the actual site, they may assume malicious websites or phishing attempts. Masking can appear deceptive and reduce user trust, especially if transparency and brand reputation are important.
- You want shareable or bookmarkable URLs: Masked domains don’t always perform well when shared or bookmarked. If the hidden frame breaks or the underlying structure of the different website changes, users might face errors after clicking the link again.
- You use SSL or advanced site security: Domain masking can interfere with SSL certificates and trigger “Not Secure” warnings. This poses risks for eCommerce sites or any platform handling sensitive data. For secure environments, replace domain masking with URL redirects that properly display meta tags and maintain encryption.
What are the key differences between domain forwarding vs masking
While both domain forwarding and masking help redirect visitors to another website, they function very differently. The difference is similar to domain redirect vs forwarding, where each serves a unique purpose and level of transparency. Forwarding sends users and search engines directly to a new destination URL, while masking keeps the displayed domain name unchanged.
Understanding these differences helps you choose the right option for SEO, usability and brand consistency.
Comparison table
| Factor | Domain forwarding | Domain masking |
| What it does | Redirects users to another URL | Displays one domain while loading content from another |
| Address bar behavior | Shows the new destination URL | Keeps the original domain visible |
| SEO value | Passes SEO authority with permanent redirects | Hides original content, offers no SEO benefits |
| Analytics tracking | Accurately tracks traffic sources | Disrupts tracking and analytics |
| Setup difficulty | Simple to configure via registrar | Slightly complex, requires frame or script setup |
| User trust | Builds transparency and reliability | May reduce trust if users notice masking |
| SSL compatibility | Fully supports SSL certificates | Often conflicts with SSL and security checks |
| Best for | Rebranding, URL changes, SEO continuity | Temporary promotions, short-term campaigns |
1. User experience
Domain forwarding provides a seamless and transparent browsing experience. When visitors type or click your old domain, they’re automatically taken to the new one, seeing the correct address in the browser’s bar. This clear redirection builds confidence and helps users easily understand they’ve reached the right website.
In contrast, domain masking keeps the same domain visible even as content changes. This can confuse visitors since the address never updates while navigating pages. It also makes sharing or bookmarking links unreliable, leading to potential usability and trust issues.
2. SEO impact
Domain forwarding, especially permanent 301 redirects, transfers SEO value from the old domain to the new one. Search engines recognize the redirect, consolidate ranking signals and maintain your site’s authority. This approach preserves your search visibility after rebranding, migrating or restructuring a website.
Also read: SEO Marketing Packages and Plans
Domain masking doesn’t pass any SEO value because search engines can’t see the real content source. It hides pages within frames or scripts, often resulting in duplicate content and indexing problems. Over time, this can reduce organic reach and prevent your site from ranking effectively.
3. Setup complexity
Setting up domain forwarding is quick and straightforward. Most domain registrars or hosting dashboards include easy redirect options where you can choose between temporary or permanent forwarding. Once configured, the system automatically routes users and search engines to the new URL.
Domain masking requires more technical steps. It often uses HTML frames, meta refresh tags or JavaScript to display another website under your chosen domain. Small errors in configuration can cause blank pages, broken layouts or frame conflicts, making masking slightly more complex to manage for non-technical users.
4. URL visibility
With domain forwarding, the browser’s address bar always shows the true destination URL. This transparency helps users confirm they’re on the right page and builds trust in the browsing experience. It also makes URLs easy to share, bookmark and reference across campaigns or platforms.
Masking, however, hides the real address. No matter which page visitors navigate to, the displayed domain remains unchanged. This might look clean for branding but sacrifices clarity and transparency, leaving users unaware of where the content is actually coming from.
5. Analytics and tracking
Forwarding works seamlessly with analytics platforms such as Google Analytics or UTM tracking links. It records accurate visitor data, including traffic sources, page performance and conversions. This helps you make data-driven marketing and SEO decisions based on reliable reports.
Domain masking interferes with analytics since all visits appear under the same masked domain. It prevents proper tracking of individual pages, user behavior and campaign effectiveness. Without visibility into these metrics, evaluating performance or improving user experience becomes difficult.
6. Security and privacy
Domain forwarding fully supports SSL certificates and HTTPS encryption, ensuring secure data transmission between the server and users. Visitors see a secure connection and trust the redirected website, which is critical for online stores or sites handling sensitive information.
Also read: A Guide to Free SSL Certificates with Let’s Encrypt
Masking often creates SSL conflicts because the visible domain doesn’t match the hidden source’s certificate. This mismatch triggers “Not Secure” warnings in browsers, discouraging visitors from continuing. It can also prevent encrypted communication, putting user trust and data privacy at risk.
While both domain forwarding and masking help connect one domain to another, forwarding is the more secure, SEO-friendly and transparent option for most businesses. Masking can be useful for short-term branding or promotions but should be used cautiously to avoid performance, tracking and trust issues.
Final thoughts
A domain is more than just an address, it’s your brand’s online identity. Choosing between domain forwarding and masking determines how users experience and trust that identity. While forwarding supports SEO and redirects visitors seamlessly, masking keeps URLs clean and consistent for short-term needs.
Each method serves a purpose, but knowing when and how to use them ensures your visitors land exactly where you want them to, without confusion or lost visibility. The goal is always to build trust, maintain clarity and protect your brand presence.
Ready to manage your domains the right way? Get started with Bluehost domain services, including domain privacy, protection and easy forwarding tools, to keep your brand secure and consistent across every click.
FAQs
Yes. 301 domain forwarding helps SEO because it passes link equity and signals to the new URL. Temporary 302 redirects do not pass full SEO value, so use them only for short-term changes.
Usually, yes. Domain masking prevents search engines from understanding your website, blocks canonical signals and can lower rankings. Google recommends forwarding instead of masking.
There’s no difference, domain forwarding is a type of redirect. In SEO terms, people search for this as domain forwarding vs redirect SEO, but they refer to the same process (typically a 301 redirect).
Yes. Masking keeps the displayed URL the same, even though the content is coming from another site. It’s useful for short-term campaigns but not recommended for SEO.
Absolutely. Many brands forward alternate TLDs (.net, .org) and typos to their main site to protect traffic and maintain consistency.
Write A Comment