Key highlights
- MultiPHP INI Editor is the fastest method to increase memory limits in cPanel without editing files manually.
- 256M works for most WordPress sites, including page builders, moderate plugins, and WooCommerce stores.
- Four configuration methods exist: MultiPHP INI Editor (primary), .user.ini, php.ini, and .htaccess (Apache only).
- Host limitations can override settings—contact support or upgrade your plan if changes don’t apply.
- Always verify changes by checking phpinfo() or WordPress Site Health after configuration.
The “Fatal error: Allowed memory size exhausted” message is one of WordPress’s most frustrating errors. It crashes sites mid-import, freezes backup operations and prevents page builders from saving layouts.
The culprit? A PHP memory limit set too low for what modern WordPress sites actually need. WordPress core technically runs on 64M, but page builders like Elementor, WooCommerce operations, and import tools push requirements far beyond that baseline.
This guide covers four proven methods to increase PHP memory limits in cPanel, ranked by reliability and ease of implementation. You’ll learn the fastest approach (MultiPHP INI Editor) plus three fallback methods for different hosting setups.
First, let’s understand what PHP memory limits are and why they matter for your site’s performance.
Use this table to pick the fastest method your hosting setup supports.
| Method (fastest → fallback) | Where you change it | What you do (1 line) | When to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| MultiPHP INI Editor (Recommended) | cPanel → Software | Select domain → set memory_limit → Apply | Best for most cPanel users |
| .user.ini | Site root (File Manager/FTP) | Add memory_limit = 256M in .user.ini | If MultiPHP INI Editor isn’t available |
| php.ini | Site root or home directory | Edit/add memory_limit = 256M | If host supports local php.ini |
| .htaccess (Apache + mod_php only) | Site root | Add php_value memory_limit 256M | Only on older Apache mod_php setups |
| wp-config.php (WordPress request limit) | WordPress root | Define WP_MEMORY_LIMIT / WP_MAX_MEMORY_LIMIT | If you can’t change server settings |
What is the PHP memory limit?
The PHP memory limit defines how much server RAM each script can consume during execution. WordPress core runs on 64M, but modern sites need significantly more.
Modern WordPress tasks often need more memory because they can involve:
- Page builders loading heavier libraries and assets
- eCommerce plugins processing checkout, payments, and inventory sync
- Import/migration tools handling large datasets and bulk database writes
Result: memory demand can exceed the minimal 64M baseline, triggering “memory exhausted” errors during heavier tasks.
When scripts exceed their allocated memory, PHP kills them immediately. The result?
Memory‑exhausted errors, white screens, or operations that complete halfway and leave databases in inconsistent states.
The challenge is finding the right balance. Too low causes failures, while a higher memory_limit doesn’t use more RAM by itself. Instead, it can allow heavier scripts to run. So, if you keep hitting the limit, find the plugin or task causing it rather than endlessly raising the cap.
How do I check my current PHP memory limit?
Before making any changes, you need to know your current memory limit. Two reliable methods exist: the phpinfo() function for precise server-level data and WordPress Site Health for quick dashboard access.
Using the phpinfo() method is the most reliable way to verify your PHP memory limit in cPanel, as it displays live server configuration rather than cached data.
While WordPress Site Health provides quick diagnostics, it may not always reflect the current settings after you’ve made changes to increase PHP memory limit in cPanel.
1. Use phpinfo() for accurate results
To check server configuration:
- Create a file named info.php in your site root.
- Add this code:
<?php phpinfo(); ?> - Visit [yoursite].com/info.php in your browser.
- Search for “memory_limit” (Ctrl+F).
- Delete the file immediately after checking.
Why this method matters: WordPress admin panels sometimes show cached values. The phpinfo() method reveals actual server configuration, not what WordPress thinks it can request.
2. Check WordPress Site Health (WordPress only)
For quick checks without file creation:
- Navigate to Tools → Site Health in WordPress.
- Click the Info tab.
- Expand the Server section.
- Look for PHP memory limit value.
Keep in mind Site Health sometimes displays cached values or WordPress’s requested limit rather than actual PHP limits. Use phpinfo() when troubleshooting persistent errors.
How to increase PHP memory limit in cPanel?
Most cPanel hosts let you raise the PHP memory_limit in a few different ways. Start with MultiPHP INI Editor because it’s the fastest and least error‑prone option. If it isn’t available on your plan or server setup, use the fallback methods in the next sections.
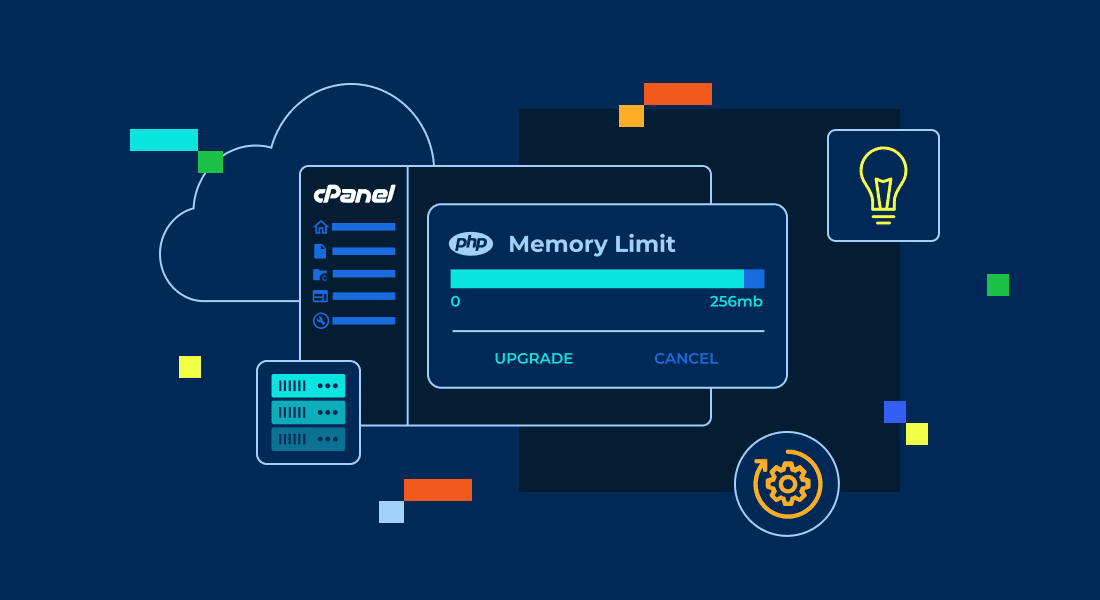
Method 1 (recommended): Increase PHP memory limit using MultiPHP INI Editor
cPanel’s MultiPHP INI Editor provides the most straightforward path to updating PHP settings. Changes apply instantly without FTP uploads, file editing or syntax mistakes. The interface validates input before applying changes.
Bluehost includes MultiPHP INI Editor in cPanel across its WordPress hosting plans, so you can update memory_limit without extra fees or advanced technical steps. The interface integrates directly with Bluehost’s Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, ensuring configuration changes propagate instantly across the server network.
Steps to increase memory limit in cPanel using Bluehost
- Log in to your Bluehost Account Manager, then click Hosting → cPanel.
- Navigate to the Software section.
- Click MultiPHP INI Editor.
- Select the Basic Mode tab.
- Choose your domain from the dropdown (or Home Directory for account‑wide).
- Scroll to memory_limit.
- Enter your value (example: 256M).
- Click Apply.
The change takes effect immediately. No waiting period, cache clearing, or server restart required.
Pro tip: Configure limits individually when running multiple sites. A simple blog doesn’t need the same resources as a WooCommerce store with hundreds of products.
When to use Editor Mode instead
Switch to Editor Mode when:
- Basic Mode doesn’t show your needed directive.
- You want to add custom PHP settings.
- You need raw php.ini syntax access.
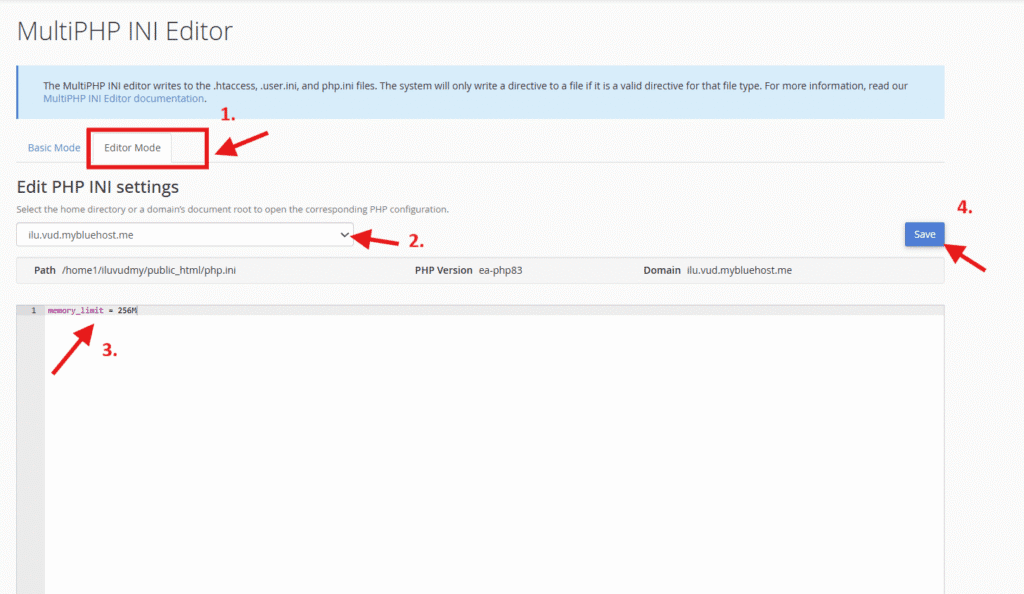
To use Editor Mode:
- Click the Editor Mode tab.
- Select your domain.
- Add directives using format:
memory_limit = 256M - Save changes.
Most users never need Editor Mode for memory adjustments. Stick with Basic Mode unless you’re comfortable with PHP configuration syntax
Method 2: Increase PHP memory limit with a .user.ini file
Modern hosting environments using PHP-FPM or CGI handlers typically accept .user.ini files for per-directory PHP overrides. This method works when MultiPHP INI Editor isn’t available.
The .user.ini approach gives direct control over configuration without cPanel access. This helps when managing sites through command-line tools or when working with hosting providers who limit cPanel features.
How to create or edit .user.ini
- Connect via FTP, SFTP or cPanel File Manager.
- Navigate to site root (usually public_html/).
- Create or open .user.ini file (note the leading dot).
- Add line:
memory_limit = 256M - Save with Unix‑style line endings (LF, not CRLF).
- Wait 5 minutes for changes to propagate.
Why the wait? PHP-FPM caches .user.ini files for several minutes to reduce disk I/O during high traffic.
Verify .user.ini is working
After 5 minutes, check phpinfo() for the memory_limit value. If it matches your .user.ini setting, the method worked.
If unchanged after 10 minutes: Your host likely doesn’t honor .user.ini files. Try MultiPHP INI Editor or contact support to determine allowed configuration methods.
Method 3: Increase PHP memory limit by editing php.ini
The php.ini file controls PHP configuration for the scope your host allows (per-directory/per-account on shared hosting; server-wide on VPS/Dedicated).
When available, editing php.ini provides comprehensive configuration control. Changes affect all PHP scripts in the same directory tree unless overridden by more specific files.
Locate php.ini in cPanel
Option A: File Manager
- Log in to your Bluehost Account Manager, then click Hosting → cPanel.
- Open File Manager, then Settings.
- Enable “Show Hidden Files”.
- Navigate to site root.
- Look for php.ini.
Option B: Home directory
Some hosts place php.ini one level above public_html. Check your account’s home directory if site root doesn’t contain one.
Option C: Create local php.ini
If no php.ini exists and your host allows it:
- Create file named php.ini in site root.
- Add your directives.
- Test immediately to confirm processing.
Not all hosts respect user-created php.ini files. Security policies sometimes force all configuration through MultiPHP INI Editor.
Edit the memory_limit directive
- Open php.ini in a text editor.
- Find line:
memory_limit = 128M (or current value) - Change to:
memory_limit = 256M - Save file.
- Verify with phpinfo().
Important: Shared hosts often override user php.ini files with server-level settings. When edits don’t apply, use MultiPHP INI Editor instead.
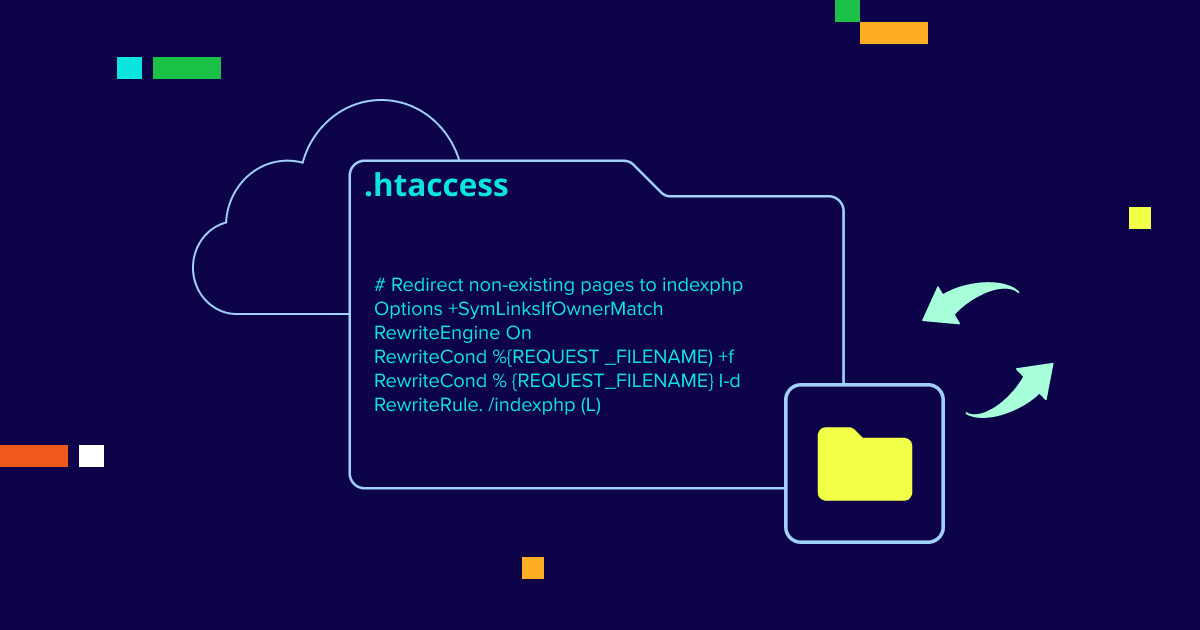
Method 4: Increase PHP memory limit via .htaccess (Apache + mod_php only)
The .htaccess approach only works on Apache with mod_php. Most modern hosting uses PHP-FPM for performance, making this method obsolete in many cases.
However, some older shared hosting setups still use Apache with mod_php. When available, .htaccess configuration applies instantly without waiting for cache expiration.
Add the directive to .htaccess
- Log in to your Bluehost Account Manager, then click Hosting → cPanel.
- Open File Manager.
- Go to your site root (usually public_html).
- Open .htaccess (create it if missing).
- Add this line:
php_value memory_limit 256M - Save the file, then recheck via phpinfo().
Changes apply to the next PHP request immediately.
Use IfModule wrapper for safety (recommended)
To prevent errors on non‑mod_php servers:
<IfModule php_module> php_value memory_limit 256M </IfModule>For PHP 7.x specifically, use:
<IfModule php7_module> php_value memory_limit 256M </IfModule>- PHP 7.x commonly uses php7_module.
- PHP 8+ uses php_module.
The IfModule wrapper ensures Apache ignores the directive gracefully when the specified module isn’t loaded, preventing configuration errors.
What if this breaks your site?
If you see 500 Internal Server Error:
- Your server doesn’t run PHP as mod_php
- Open .htaccess immediately
- Remove the php_value lines
- Save file
Your site should recover within seconds. Switch to MultiPHP INI Editor or .user.ini instead.
How to increase WordPress memory limit in wp-config.php?
WordPress provides its own memory management layer between your site and PHP’s hard limits. Two constants in wp-config.php tell WordPress how much memory to request.
This approach works well when server configuration access is restricted. It also allows different limits for frontend versus admin operations, which is useful since admin tasks consume more resources.
Add WP_MEMORY_LIMIT to wp-config.php
- Connect via FTP or File Manager.
- Open wp-config.php from WordPress root.
- Find line:
/* That's all, stop editing! Happy publishing. */ - Add above that line:
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M'); - Save file.
This controls memory for normal frontend operations (page loads, widgets, plugins).
Add WP_MAX_MEMORY_LIMIT for admin tasks
Admin operations (updates, imports, media processing) need extra headroom.
- Add line below WP_MEMORY_LIMIT:
define('WP_MAX_MEMORY_LIMIT', '512M'); - Save file.
Now admin tasks can request up to 512M while frontend caps at 256M.
Reality check: WordPress can only request memory PHP actually allows. Setting WP_MEMORY_LIMIT to 512M does nothing if your host caps PHP at 256M. Check server’s PHP memory_limit (using phpinfo) before setting WordPress constants higher.
What memory limit value should I set (128M vs 256M vs 512M)?
The right memory limit depends on your site’s complexity and the operations you run. Too low causes crashes and incomplete operations. Too high wastes server resources and masks underlying code problems.
Start with 128M for typical WordPress installations. Monitor error logs for several days. Increase only when logs show specific memory exhaustion during identifiable operations like imports or bulk edits.
| Site type | Recommended limit | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Basic blog (minimal plugins) | 128M | WordPress core with lightweight theme operates efficiently |
| Standard WordPress site | 256M | Handles page builders, contact forms, typical plugin collections |
| WooCommerce store | 256M – 512M | Product imports, inventory sync, payment processing demand more |
| Heavy page builder sites | 512M | Elementor, Divi, Visual Composer with complex layouts consume significant memory |
| Import/migration tasks | 512M+ | Large database operations, media migrations require substantial headroom |
Don’t ignore the root cause
Raising memory limits treats symptoms, not diseases. Sites needing constant increases usually have underlying code problems.
Common culprits include:
- Poorly optimized plugins loading entire datasets instead of paginating
- Unoptimized images processed on every page load
- Inefficient database queries returning thousands of rows when twenty would suffice
- Background tasks without proper memory management
Check error logs to identify which plugins trigger errors most frequently. Disable them systematically to isolate problematic code.
Fixing actual problems produces faster, more stable sites than continually raising limits.
How do I verify my PHP memory limit change worked?
Configuration changes don’t always apply as expected in hosting environments. Multiple settings files can override each other. Server-level restrictions might prevent changes entirely.
Verification confirms your adjustment actually modified PHP’s behavior. This step takes 60 seconds but saves hours of frustrated troubleshooting.
Verification checklist
Method 1: Check phpinfo()
- Create info.php file.
- Visit yoursite.com/info.php.
- Search for “memory_limit”.
- Check the Local Value column.
- Delete info.php immediately (security risk).
Method 2: WordPress Site Health
- Go to Tools → Site Health.
- Click the Info tab.
- Expand the Server section.
- Verify PHP memory limit.
Method 3: Test the original error
- Retry the operation that previously failed (import, backup, page builder save).
- Successful completion confirms your memory increase resolved the problem.
- Check error logs afterward to ensure no new memory warnings appeared.
Why you might still hit the PHP memory limit after increasing it?
Configuration changes sometimes fail despite following correct procedures. Multiple factors can prevent your settings from taking effect, ranging from host-imposed restrictions to configuration file conflicts.
Understanding common failure points helps you troubleshoot effectively when initial attempts don’t work. Some issues relate to hosting limitations while others stem from code-level problems.
Most common causes
- Host-imposed maximum
Shared hosting plans enforce strict memory caps for server stability. Your provider may limit all accounts to 256M regardless of configuration file settings.
Solution: Contact Bluehost support to confirm your plan’s maximum. Upgrade to VPS or dedicated hosting when sites legitimately need more than shared plans allow.
- Per-directory override
PHP configuration cascades through directory hierarchies. A php.ini or .user.ini file in a parent directory can override subdirectory settings.
Solution: Check for configuration files in directories above site root. Remove conflicting directives or consolidate into most specific location.
- Wrong domain selected
MultiPHP INI Editor’s domain dropdown is easy to overlook. Selecting “Home Directory” applies account-wide instead of to specific sites.
Solution: Double-check dropdown selection before clicking Apply. Verify you configured the domain actually throwing errors.
- PHP version mismatch
Servers often run multiple PHP versions simultaneously. Your site might execute under PHP 8.0 while you modified PHP 7.4 configuration.
Solution: Verify site’s active PHP version through MultiPHP Manager or phpinfo(). Match configuration to exact version handling requests.
Final thoughts
Increasing PHP memory limits in cPanel takes minutes using the right method for your hosting environment. MultiPHP INI Editor provides fastest, most reliable results with immediate application and zero file editing.
The .user.ini and php.ini methods offer alternatives when MultiPHP INI Editor isn’t available. The .htaccess approach works only in specific Apache + mod_php configurations becoming increasingly rare.
Most WordPress sites run smoothly with 256M. WooCommerce stores and page builder-heavy sites may need 512M. Always verify changes through phpinfo() or WordPress Site Health.
Ready to stop fighting memory limit errors?
Start with Bluehost WordPress hosting, which gives you cPanel access to MultiPHP INI Editor for quick PHP memory limit changes. If you consistently hit your plan’s cap or run resource-heavy workloads, upgrade to VPS hosting for higher limits and deeper server control.
FAQs
Open MultiPHP INI Editor from Software section. Select your domain, find memory_limit, enter value like 256M, click Apply. Changes take effect immediately without file editing or FTP access.
Most shared hosts don’t expose php.ini directly because manual editing risks breaking sites. MultiPHP INI Editor provides safer interface with input validation. When hosts provide access, check home directory (one level above public_html) or site root.
Only on Apache servers running PHP through mod_php. Add php_value memory_limit 256M to site root .htaccess. Modern hosting uses PHP-FPM instead, making MultiPHP INI Editor more reliable.
On Bluehost, 256MB is commonly the default and 128MB is a widely recommended baseline, but the maximum you can set depends on your specific plan/server. Verify the effective limit in phpinfo() (Local Value) or confirm the cap with support.
No. Raising memory_limit doesn’t consume additional memory unless scripts actually need it. The setting defines maximum available, not default usage. Set responsibly based on actual site requirements.
Yes. MultiPHP INI Editor’s domain dropdown lets you configure each site independently. Select individual domains for site-specific settings or Home Directory for account-wide configuration.
Write A Comment