Key highlights
- Learn how to securely change MySQL user passwords using proper SQL syntax and best practices.
- Understand how to manage root password resets safely across different operating systems.
- Discover when to use statements like ALTER USER or SET PASSWORD for smooth account management.
- Find out how to use Administrative Tools and Services Manager to manage your MySQL server efficiently.
- Explore essential steps to verify changes, reload privileges and keep your MySQL environment secure.
To change a MySQL user password in cPanel, follow these simple steps:
- Step 1: Log in to your account manager and open the Hosting section from the left menu.
- Step 2: On the hosting details page, select the cPanel button.
- Step 3: Your cPanel dashboard will open in a new tab.
- Step 4: Inside cPanel, navigate to the Databases area and choose MySQL Databases.
- Step 5: On the MySQL Databases page, scroll to the MySQL Users section.
- Step 6: In the list of users, find the username you want to update in the list of existing users.
- Step 7: Select the Change Password option next to that user.
- Step 8: Enter the new password you want to use.
- Step 9: Save the update by clicking Change Password.
That’s it. Your MySQL user password is now updated!
While the process is quick, it’s also important to understand why keeping your database credentials secure matters. MySQL is one of the most widely used open-source database systems, powering everything from small blogs to large eCommerce stores. It plays a vital role in storing and managing your website’s data safely.
A weak or outdated password can expose your database to unauthorized access or data loss. That’s why regularly reviewing and updating your MySQL user credentials is one of the simplest ways to strengthen security.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to change a MySQL user password using two simple methods through cPanel tools and SQL commands. We’ll also explain how to change MySQL user password and cover the MySQL change password for user command line method for advanced users.
Why do we need to change MySQL user passwords regularly?
Websites that connect to a MySQL database rely on secure user credentials to keep data protected. Each MySQL user account defines who can access your MySQL server and what actions they can perform. When passwords become weak, they can create security gaps that allow unauthorized access and put your website data at risk.
Here’s why updating your MySQL user password regularly is essential:
- Supports website maintenance: Updating passwords during site migrations, role changes or configuration updates helps maintain uninterrupted database connections.
- Strengthens account security: A strong, updated password helps prevent unauthorized access and keeps your user account protected.
- Prevents data breaches: Regular password changes reduce the chances of exploitation through stolen or leaked credentials.
- Maintains access control: Updating credentials ensures only trusted users can log in and manage your MySQL database securely.
- Fixes common access issues: Resetting the root password can restore access to your MySQL service when authentication issues prevent you from logging in.
Consistent password management not only protects sensitive data but also improves the reliability and performance of your database server. To continue keeping your database secure, let’s explore the different methods you can use to change a MySQL user password.
What are the different methods to change a MySQL user password?
There are a few ways to update or reset a MySQL user password, depending on your level of access and technical comfort. Each method works toward the same goal of keeping your MySQL server secure and ensuring only authorized users can connect.
The two most common methods are:
- Changing the password through cPanel: This is the simplest and most accessible option for most website owners. You can manage user accounts, reset passwords and maintain account security directly through your hosting dashboard without using commands.
- Changing the password through SQL commands or terminal: This method is preferred by developers or system administrators who have SSH access or manage VPS environments. It involves using the terminal to connect with the MySQL server and there are two ways to do this:
- By entering the MySQL shell and running SQL commands such as ALTER USER or SET PASSWORD.
- By using the mysqladmin command, which allows you to update the password directly from the terminal without logging into MySQL.
Both command-line methods achieve the same result. The main difference lies in the level of control and the tools you used for the update. Since most users prefer a simpler approach, we’ll begin with the easier option of changing your MySQL user password through cPanel.
How can we change a MySQL user password in cPanel?
Using cPanel is one of the easiest ways to update your MySQL user password. The interface allows you to manage databases and user accounts without needing to run SQL commands manually. If you’re new to managing a MySQL server, this method is reliable, quick and beginner friendly.
Follow these steps to change your MySQL user password through cPanel.
Step 1: Access the MySQL Databases section
- Start by signing in to your account manager. Once logged in, select Hosting from the left-hand navigation panel to access your hosting settings.
- After opening your hosting details, click the cPanel button to move into your hosting control panel.
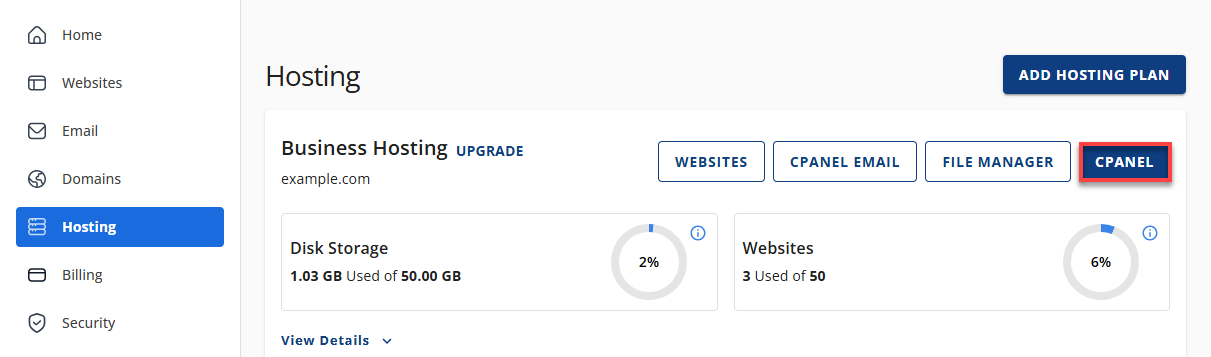
- cPanel will load in a separate browser tab, giving you access to your site’s files and database tools.
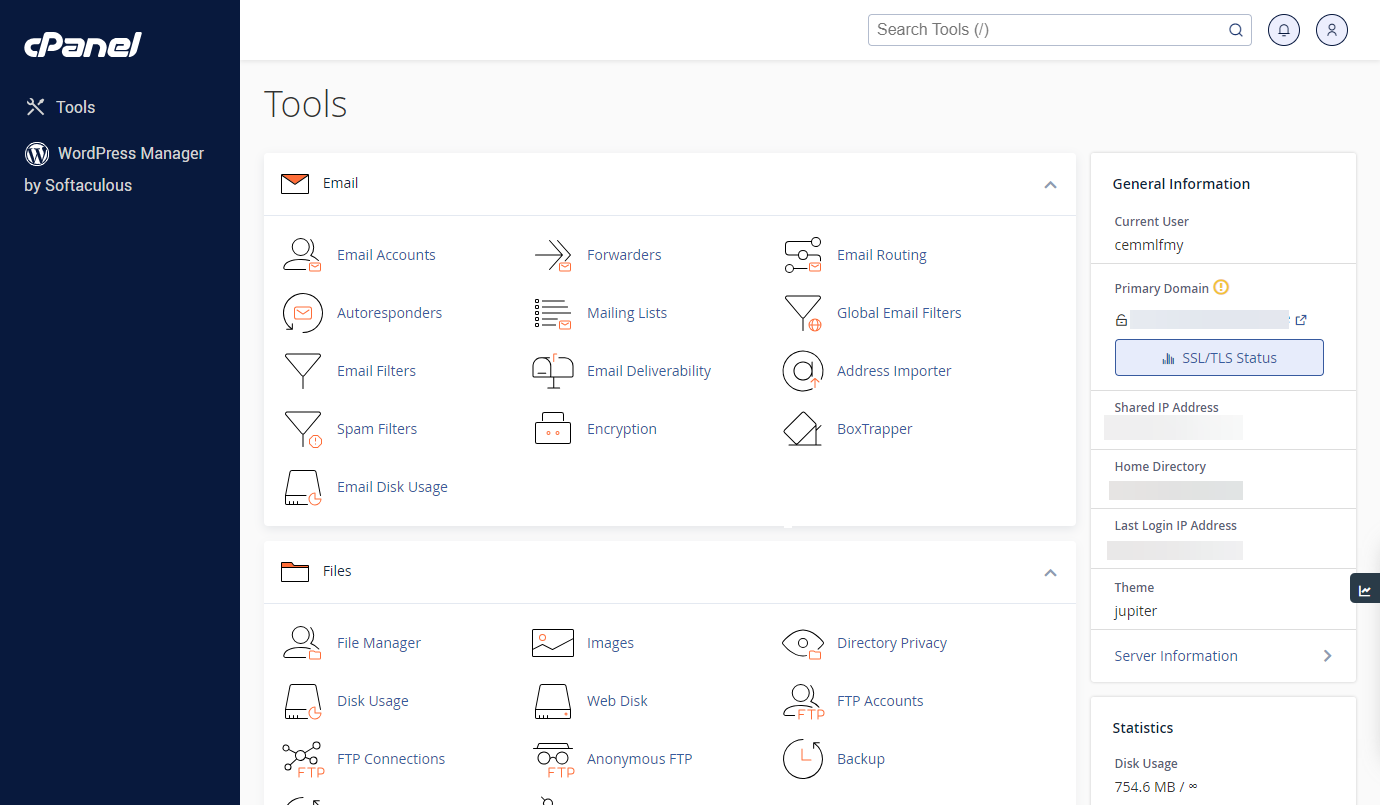
- Scroll down to the Databases section and select MySQL Databases.
The MySQL Databases tool is where you can view, edit or remove database users. It also lets you perform essential tasks like adding new databases, adjusting permissions and resetting user passwords.
Once you’ve accessed this section, your next step is to locate the user account that needs a password update.
Also read: How to Manage Databases with Applications
Step 2: Locate the MySQL user account
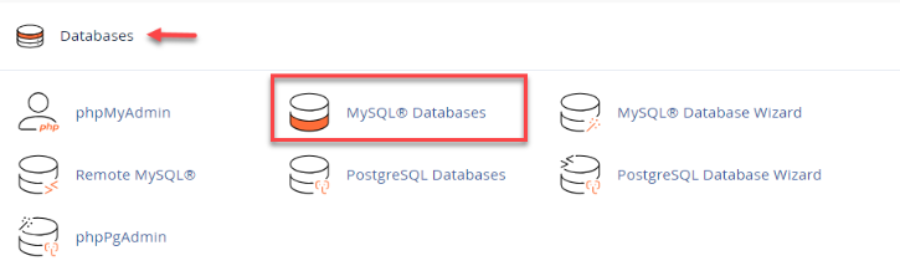
After opening the MySQL Databases page, you’ll see a few different areas for database management. The Current Users or MySQL Users section lists all the usernames associated with your hosting account.
- Within your cPanel dashboard, scroll to the Databases section and click on MySQL Databases to manage your MySQL settings.
- Once inside the MySQL Databases area, move down the page until you reach the section labeled MySQL Users.
- Review the list of users displayed and identify the account whose password you want to update.
Each user account is assigned specific privileges that control how it connects to your MySQL server. Identifying the correct account ensures that you update credentials for the right user and maintain secure authentication settings.
When you’ve found the correct username, you’re ready to change the password.
Step 3: Change the password
Now that you’ve identified the user, you can update their credentials directly in cPanel.
- Click the Change Password link next to the chosen username to begin updating the credentials.
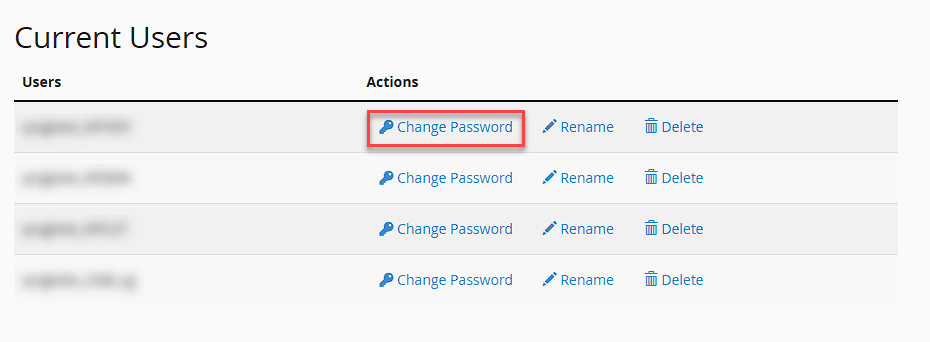
- Type in the new password you wish to assign to the selected MySQL user account.
- Confirm the update by selecting Change Password, which applies the new credentials immediately.
Pro tip: Choose a strong password that combines uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols. You can also use a password generator for added protection.
Once you save the changes, cPanel automatically updates the credentials. Your MySQL database will start recognizing the new password immediately and you can continue managing your site without any additional steps.
By completing these steps, you’ve successfully changed your MySQL user password through cPanel. Next, we’ll explore how to perform the same task using SQL commands for users who prefer manual control.
How can we change a MySQL user password using SQL commands (for advanced users)?
If you prefer working directly through the terminal or have SSH access, you can use the MySQL change user password command line method. It allows you to change a MySQL user password manually using SQL statements for complete control. Before running any command, make sure you use the correct MySQL change user password syntax for your MySQL version to avoid errors.
Additionally, this method gives you more control over user accounts, privileges and database configurations within your MySQL server. Here’s how to update the password safely.
Also read: What is SSH Access and How to Enable It in Your Hosting Account
Step 1: Log in to MySQL
Start by accessing your MySQL command line. Use the following command to log in as the root user or an administrative account:
mysql -u root -p
You will be prompted to enter your existing root password or the password for the user account you’re logging in with.
Step 2: Select the MySQL database
Once logged in, select the internal MySQL database that stores all user information and authentication details.
USE mysql;
This command switches the session to the correct database, allowing you to manage user credentials and access permissions.
Step 3: Run the appropriate command based on MySQL version
The command used to change a password depends on your MySQL version.
For MySQL 5.7.6 and later, run:
ALTER USER 'username'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password';
For older MySQL versions, use:
SET PASSWORD FOR 'username'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('new_password');
The ALTER USER statement is the recommended and more secure method since it follows the latest account management statements and supports newer authentication plugins.
Step 4: Apply and confirm changes
After running the command, apply your changes to ensure they take effect immediately.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
This step reloads the grant tables, so your updated password becomes active across the MySQL service.
Step 5: Exit MySQL
Once the password is updated, you can exit the MySQL shell.
QUIT;
This completes the process. Your changes are now saved and the new password is ready for use.
Using direct SQL commands gives you full control over user authentication and root access. It’s especially useful for developers managing multiple databases or troubleshooting permission-related issues within the MySQL server.
Another option is to use mysqladmin; a command-line utility that allows quick password changes outside the MySQL shell. In the next section, we’ll walk through the steps to change a MySQL password using this command.
How can we change a MySQL password using the mysqladmin command?
If you prefer using the command line, the mysqladmin command is one of the quickest ways to update a MySQL user password. It’s also commonly used when following MySQL change user password command line steps for direct terminal updates.
To change a user password, use this command:
mysqladmin -u username -p'old_password' password 'new_password'
Here’s what each part does:
- -u username: Specifies the MySQL username.
- -p’old_password’: Prompts for or includes the current password for authentication.
- password ‘new_password’: Defines the new password to set.
The mysqladmin command is available on most Unix-like systems, including Linux and macOS. It’s especially useful for root users who want to reset administrative credentials quickly.
After you run the command, the MySQL service applies the change immediately and no restart is needed. With the password now updated on the server, the next step is to ensure your website stays connected by reviewing its database settings.
How can we update your application configuration file?
After changing a MySQL user password, your website or application still needs to be updated with the new credentials. Without this step, your MySQL database and site may fail to connect properly.
Most websites store database connection details in a configuration file. This file contains the database name, username, user password and host name that your site uses to connect to the MySQL server. Updating the password here ensures your application continues to communicate with the database securely.
Below are the common configuration files for popular content management systems:
| Platform | Configuration file | Location |
|---|---|---|
| WordPress | wp-config.php | Root directory |
| Joomla | configuration.php | Root directory |
| phpBB | config.php | Root directory |
| Zen Cart | configure.php | Includes folder |
To update your configuration file:
- Open the file using your hosting File Manager or connect via FTP.
- Locate the password variable that stores your MySQL user password.
- Replace the old password with the new one you created.
- Save the file and refresh your website to apply the changes.
If this step is skipped or the password is entered incorrectly, your site may display a “database connection error.”
Updating the configuration file immediately after changing your password ensures smooth connectivity and keeps your database secure. Once the update is complete, it’s important to verify that the new MySQL password works correctly and your database connection is active.
How can we verify the MySQL password change?
After updating your MySQL user password, it’s important to confirm that the new credentials work correctly. This ensures your database connection is active and your MySQL server accepts the updated login details.
You can check the update in two simple ways:
- Log in through phpMyAdmin
- Access phpMyAdmin from your hosting control panel.
- Enter your MySQL username and the new password.
- If you can log in successfully, your user account credentials have been updated.
- Test using the command line
- Open the terminal or command prompt.
- Run the following command:
mysql -u username -p - When prompted, type the new password.
- If the connection opens without errors, the password change is complete.
If the login fails, recheck the password in your configuration file and confirm that the MySQL service is running properly. If the problem continues, there may be other configuration or authentication issues that need troubleshooting.
How to troubleshoot MySQL password and login errors?
Even after changing a MySQL user password, you might occasionally run into login or authentication issues. Most of these problems are common and can be fixed with a few simple checks. The steps below are safe to follow and won’t result in any database loss.
| Issue | Possible cause | How to fix it |
|---|---|---|
| Access denied for user | Incorrect username, host or password | Verify that you’re using the correct MySQL username, password and host (usually localhost). |
| Authentication plugin error | Outdated plugin or MySQL version mismatch | Run the ALTER USER command to reset authentication or ensure your MySQL server version supports the plugin in use. |
| Password change not applied | Privileges not reloaded | Run FLUSH PRIVILEGES to reload the grant tables and apply the new credentials. |
| Cannot log in as root user | Forgotten root password or limited permissions | Use SSH access to reset the root account password or contact your hosting provider for assistance. |
| Connection timeout or refusal | MySQL service not running | Restart the MySQL service from your control panel or terminal to re-establish access. |
If none of these solutions work, review your configuration file again to ensure the updated credentials match exactly. A single typo in the password or database name can cause connection errors.
Once you’ve verified your credentials and applied these fixes, try logging in again using phpMyAdmin or the command line to confirm that the issue is resolved. These troubleshooting steps cover the most frequent MySQL password and login errors.
If you want a more secure and reliable setup, you can also rely on our Bluehost hosting. You can get reliable database tools, automated backups and expert support whenever you need it. View our hosting plans today!
To avoid similar issues in the future, let’s look at how to prevent them by employing better password management practices.
5 Best practices we recommend for MySQL password management
Adopting strong password management practices enhances MySQL server security and ensures consistent database performance. These simple steps can strengthen your overall account security and prevent future connection errors.
1. Use strong, unique passwords for every user
Create passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols. Avoid using dictionary words or simple patterns. Each MySQL user account should have a unique password to prevent shared access and minimize security risks if one set of credentials is compromised.
2. Rotate credentials regularly
Updating your MySQL user password regularly reduces the risk of unauthorized logins. Consider changing credentials every few months or after granting temporary access to developers or third-party tools. This habit keeps your MySQL database secure and limits exposure to outdated passwords.
3. Restrict privileges only to what is necessary
Grant users only the permissions they need to perform their specific tasks. Avoid giving full administrative access to every user account, especially when managing production databases. Limiting privileges helps protect sensitive data and prevent accidental changes to critical tables or configurations.
4. Store passwords securely (avoid plaintext)
Never store passwords in plain text files or unencrypted formats. Use your hosting control panel’s built-in password manager or a dedicated secure vault to protect credentials. If your system uses environment variables or encrypted configuration files, make sure they’re updated whenever the user password changes.
5. Keep backups before making any user changes
Always back up your MySQL database before modifying user accounts or passwords. Having a recent backup allows you to restore access quickly if a connection issue or authentication error occurs during the update process. Backups are a key part of proactive password management and overall database protection.
Implementing these best practices helps maintain a secure, stable and well-organized MySQL server. Regular reviews and careful management of your user credentials will minimize risks and ensure long-term database reliability.
Final thoughts
Updating your MySQL user password is a simple and essential step in keeping your website and database secure. Whether you use cPanel or the command line, the process is straightforward and effective when followed carefully.
Maintaining consistent password hygiene helps prevent unauthorized access, data breaches and unexpected downtime. Regularly reviewing your credentials and applying best practices keeps your MySQL server stable and your site running smoothly.
At Bluehost, we make it easy to manage your MySQL databases through a secure, user-friendly hosting environment. Our tools help you update credentials, protect data and maintain consistent performance in one convenient platform.
So, explore our WordPress Hosting plans to get integrated MySQL tools, automatic updates and expert 24/7 support that keep your website performing at its best.
FAQs
To change a MySQL user password, make sure you have administrative access. These steps also apply if you’re learning how to change MySQL user password using SQL or command-line tools. The process involves three simple steps:
1. Apply an ALTER USER or SET PASSWORD statement. These follow the standard SQL syntax described in the MySQL Docs.
2. Run a flush privilege or reload privileges command, so the new credentials take effect immediately.
3. Check the server output to confirm it started successfully and that it applies to the correct user username in the user table.
Following these steps ensures your password change is applied securely and recognized across your MySQL server.
You can change a MySQL user password through the command prompt or console window, depending on your operating system.
Follow these key steps:
1. Log in as an administrator on the MySQL host or connect to the server as root.
2. Use a secure password update method such as a SET PASSWORD or ALTER USER statement, as explained in the MySQL Docs.
3. Apply changes by running flush privileges, so the new password takes effect.
If you’re using Windows operating systems, open the Start Menu and go to Administrative Tools. Then, access the Services Manager to manage your MySQL server or restart the service after the update.
You can update a password in MySQL using SQL statements designed for user management. Follow these best practices:
1. Use a password assignment statement such as ALTER USER or SET PASSWORD. These follow standard SQL syntax outlined in the MySQL Docs.
2. Avoid editing directly. Don’t modify the user table unless it’s absolutely necessary. Instead, rely on secure update methods supported by your MySQL version.
3. Check configuration details in the authentication_string password field and for localhost identified users to ensure proper access control.
4. Apply changes by running flush privileges, so the update activates across your MySQL server environment.
This ensures that the password change is applied safely and recognized by all connected users.
Yes. A MySQL user can change their own password if given read access and the right permissions. The administrator controls this in the user table through changing user password privileges.
Each Unix user or other users connected to the database can update their password securely following company policy. Refer to MySQL Docs for the recommended syntax and confirm via server output that privileges were applied correctly.
Changing the root password requires full administrative access to the MySQL server. You can manage this through system tools. This process also explains how to change root user password in MySQL safely while keeping administrative privileges intact.
This is how you do it:
1. Use Administrative Tools or the command prompt while the MySQL server runs.
2. On Windows operating systems, open the Start Menu, select Control Panel and choose Services Manager.
3. Find the Windows service running MySQL and restart it after setting up the new password.
4. Finally, reload privileges to confirm that the user root or root localhost access updates are active.
To log in as the root user, connect to the MySQL host through a console window or command prompt. You’ll need the root password created during setup. Before connecting:
1. Ensure the MySQL service starts successfully.
2. On Unix systems, log in as a Unix user with administrative rights.
3. On Windows, open Administrative Tools or use Task Manager to confirm the MySQL Init service is running.
Once connected, you can safely manage your MySQL server with full root access.
The root password is usually set during MySQL installation. If you’ve forgotten it, try the following steps:
1. Look for the log file or files named my.ini or my.cnf under Program Files where MySQL is installed.
2. Open Administrative Tools, the Services Manager or the Control Panel to confirm where the MySQL server runs.
3. Refer to the MySQL Docs for best practices on credential storage and security for Windows operating systems.
Always store your root password securely to prevent unauthorized access to the database.
If you forget your root password, you can safely reset it through your system tools. Follow these steps:
1. Restart the MySQL server manually using Administrative Tools or your system’s Task Manager.
2. Stop the Windows service, restart it with temporary access and update your login credentials.
3. Avoid the kill command unless absolutely necessary, as it may disrupt active connections.
4. Apply changes using a flush privileges statement and check the server output to confirm the service started successfully.
5. Always review the MySQL Docs for your version and host name before making server-level changes.
You can change user in the MySQL CLI by signing in with a different account. Here’s how you switch users:
1. Exit the current session before switching users.
2. Reconnect using a different user username and valid credentials.
3. Ensure the new account has the required read access or administrative rights.
4. Manage users through the user table or your system’s Administrative Tools.
5. Check the server output or connection message to confirm that MySQL started successfully with the new user.
For more details, refer to the MySQL Docs for your operating system.

Write A Comment