Vous êtes-vous déjà demandé pourquoi vous aviez besoin à la fois d’un nom de domaine et d’un site web ? Comprendre leur différence est crucial pour établir une forte présence en ligne. De nombreuses personnes confondent les concepts de noms de domaine et de sites Web, les utilisant souvent de manière interchangeable. Ce guide vous aidera à démystifier ces concepts, à expliquer comment ils fonctionnent ensemble et à vous donner des informations sur le choix des solutions de domaine et d’hébergement Web adaptées à vos besoins. Voyons donc quelle est la différence entre un domaine et un site web.
Comprendre les bases
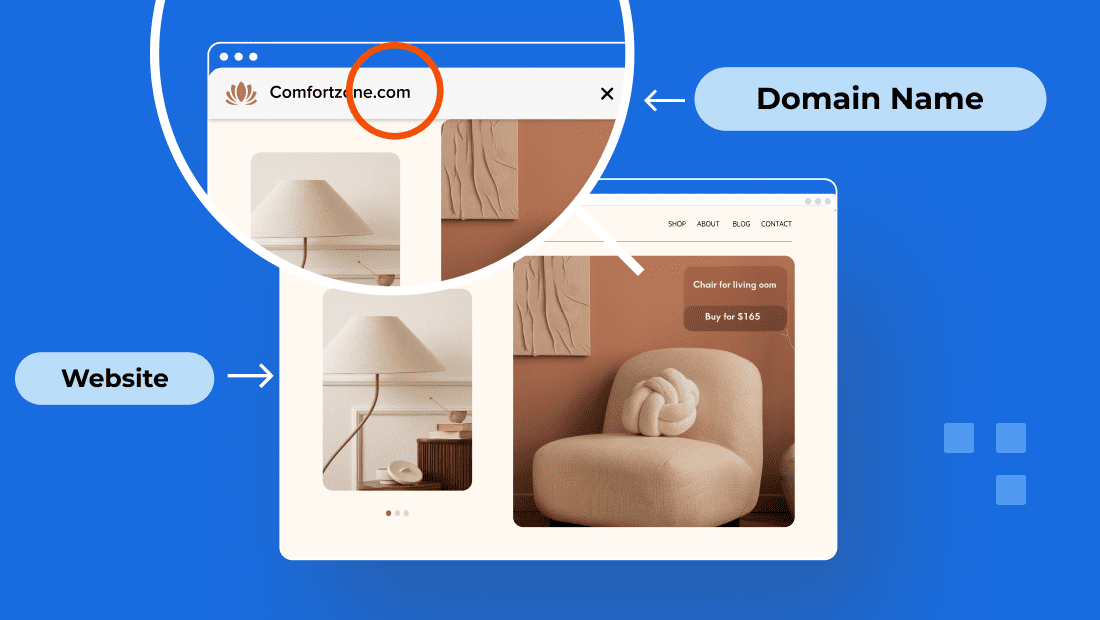
Pensez à envoyer une lettre. Vous avez besoin d’une adresse et du contenu de la lettre pour qu’elle soit livrée. Dans le monde en ligne, un nom de domaine est comme l’adresse et le site web est le contenu.
Qu’est-ce qu’un domaine ?
Un nom de domaine sert d’adresse unique à votre site Web sur Internet, ce qui permet aux utilisateurs de le trouver et d’y accéder facilement. Au lieu de se souvenir de longues chaînes de chiffres, les visiteurs tapent simplement votre domaine, comme « bluehost.com », dans la barre d’adresse de leur navigateur.
En coulisses, les ordinateurs communiquent à l’aide d’adresses IP, qui sont des identificateurs numériques complexes. Pour combler cette lacune, le système de noms de domaine (DNS) agit comme l’annuaire téléphonique d’Internet, traduisant les noms de domaine conviviaux en adresses IP lisibles par machine. Ce processus transparent garantit que les utilisateurs peuvent naviguer sur le Web sans effort sans avoir à rappeler les détails techniques.
Lorsque vous enregistrez un nom de domaine, vous revendiquez une place unique sur Internet, ce qui permet aux utilisateurs de vous trouver facilement. Avec les services de domaine de Bluehost, l’enregistrement d’un domaine se fait de manière transparente, offrant une variété d’extensions de domaine, une protection de la vie privée et des outils de gestion faciles pour établir votre présence en ligne sans effort.
Lire aussi : Qu’est-ce qu’un nom de domaine ? Tout ce que vous devez savoir
Qu’est-ce qu’un site web ?
Maintenant que nous avons parlé de l’adresse, concentrons-nous sur la destination : le site web. Un site Web est un ensemble de pages Web et de fichiers de site qui résident sur un serveur Web. Chaque page contient du contenu tel que du texte, des images, des vidéos et des éléments interactifs.
Considérez un site Web comme un magasin physique. Tout comme un magasin a différentes sections et affichages, un site Web a plusieurs pages organisées pour une navigation facile. Des hyperliens relient ces pages, guidant les visiteurs à travers le contenu de manière transparente.
L’objectif d’un site Web peut varier considérablement : il peut s’agir d’une boutique de commerce électronique, d’un blog ou d’un portfolio. Quelle que soit sa fonction, un site web sert de plate-forme pour présenter des informations, des produits ou des services au monde en ligne. Bluehost fournit des services d’hébergement Web haute performance, y compris l’hébergement partagé, VPS, dédié et cloud, garantissant que votre site Web reste rapide, sécurisé et accessible à tout moment.
Lire aussi : Est-il facile de créer un site Web ? + Réponses à d’autres questions
Enregistrement de domaine vs hébergement web : quelle est la différence ?
Lors de l’établissement d’une présence en ligne, il est essentiel de comprendre la distinction entre l’enregistrement de domaine et l’hébergement Web et la différence entre le site Web et le domaine. Un nom de domaine est comme une adresse postale, dirigeant les utilisateurs vers un emplacement spécifique sur Internet, tandis que l’hébergement Web est l’espace réel où les fichiers, les données et le contenu de votre site Web sont stockés.
L’enregistrement d’un domaine vous donne le droit exclusif d’utiliser ce nom, mais il n’inclut pas le stockage ou les fonctionnalités d’un site Web. Pour rendre votre site accessible en ligne, vous avez besoin d’un fournisseur d’hébergement qui stocke les fichiers de votre site Web sur un serveur et les livre aux visiteurs lorsqu’ils entrent dans votre domaine dans leur navigateur.
De nombreuses entreprises achètent d’abord un domaine, même si elles n’ont pas encore de site Web, pour sécuriser leur identité de marque. L’hébergement Web, en revanche, est essentiel lorsque vous êtes prêt à lancer un site Web et que vous avez besoin d’un endroit fiable pour stocker les données de votre site en toute sécurité.
Quelle est la différence entre un domaine et un site web ?
Voici la différence entre un site Web et un domaine :
| Caractéristique | Domaine | Site internet |
| Définition | L’adresse que les utilisateurs saisissent pour accéder à un site web | Une collection de pages Web et de contenus |
| But | Identifie l’emplacement en ligne du site Web | Affiche et organise le contenu pour les visiteurs |
| Dépendance | Peut exister sans site web | Besoin d’un domaine pour être accessible |
| Exemple | google.com | Moteur de recherche de Google et autres services |
| Géré par | Bureaux d’enregistrement de domaines (par exemple, Bluehost) | Fournisseurs d’hébergement Web (par exemple, Bluehost) |
Le rôle des domaines et des sites web dans l’identité en ligne
Un domaine sert d’identité numérique, ce qui permet aux utilisateurs de vous trouver plus facilement. Cela donne à votre marque de la crédibilité et un aspect professionnel, ce qui est crucial pour les entreprises et l’image de marque personnelle.
Comment les domaines servent d’adresse numérique
Les domaines simplifient la navigation sur Internet. Au lieu de se souvenir d’une adresse IP telle que « 192.168.1.1 », les utilisateurs peuvent taper un nom facile à mémoriser comme « bluehost.com » pour accéder à un site Web. Posséder un domaine permet aux entreprises de créer des adresses e-mail de marque (par exemple, [email protected]), améliorant ainsi le professionnalisme.
Lire aussi : Comment fonctionnent les domaines ? Le guide ultime
Les sites web comme incarnation de votre présence en ligne
Votre site Web est l’endroit où les visiteurs interagissent avec votre marque. Il héberge votre contenu, vos produits, vos services et vos éléments interactifs, ce qui en fait un élément crucial de votre empreinte numérique. Un site Web bien conçu améliore l’expérience utilisateur et peut aider à améliorer les classements SEO, augmentant ainsi la visibilité en ligne.
Lisez aussi : Exemples de sites Web WordPress pour l’inspiration et les conseils
Relation entre les domaines et les sites web
Pouvez-vous avoir un domaine sans site web ?
Oui. De nombreuses entreprises et particuliers enregistrent des noms de domaine à l’avance pour sécuriser leur identité en ligne, même s’ils n’ont pas encore de site Web. Les domaines peuvent également être utilisés pour les adresses e-mail ou redirigés vers d’autres plateformes en ligne, telles que les pages de médias sociaux ou les pages de destination temporaires.
Le processus de liaison de domaines à des sites Web
Pour rendre votre site Web accessible, vous devez connecter le domaine à un plan d’hébergement. Ce processus implique la mise à jour des paramètres DNS pour connecter le nom de domaine au service d’hébergement Web où les fichiers de votre site Web sont stockés. Sans cette étape, un nom de domaine seul n’affichera pas un site web. Si votre domaine et votre hébergement Web se trouvent sur des plateformes différentes, vous devrez peut-être suivre des étapes supplémentaires.
Lire la suite : Comment connecter un domaine à un hébergement en utilisant différents fournisseurs
Bluehost : Votre solution unique pour les domaines, l’hébergement et le site web
Bluehost offre une gamme complète de services pour établir et améliorer votre présence en ligne, y compris l’enregistrement de domaines et diverses solutions d’hébergement adaptées à divers besoins.
Enregistrement de domaine
La sécurisation d’un domaine est la première étape de la construction de votre identité en ligne. Les services de domaine de Bluehost simplifient ce processus en fournissant un outil de recherche de domaine intuitif, vous permettant de trouver et d’enregistrer le nom de domaine parfait qui représente votre marque. Ils offrent une large gamme d’extensions de domaine, y compris des options populaires telles que .com, .net et .org, ainsi que des extensions plus récentes telles que .tech, .store et .blog. De plus, Bluehost fournit une gestion de domaine facile via un panneau de contrôle convivial, vous permettant de gérer efficacement la redirection de domaine, la gestion DNS et d’autres paramètres essentiels.
Lire la suite : Nom de domaine gratuit | Comment obtenir un nouveau domaine pour 0 $ chez Bluehost
Solutions d’hébergement web
Une fois votre domaine enregistré, le choix du bon plan d’hébergement est crucial pour les performances et l’évolutivité de votre site web, en particulier en mettant l’accent sur l’optimisation des moteurs de recherche. Bluehost propose plusieurs options d’hébergement :
- Hébergement partagé : Idéal pour les débutants et les petits sites Web, l’hébergement partagé permet à plusieurs sites de partager les ressources du serveur, ce qui en fait une solution rentable. Les plans d’hébergement partagé de Bluehost sont livrés avec des fonctionnalités telles qu’un domaine gratuit pour la première année, un CDN gratuit, un certificat SSL gratuit et une installation WordPress en un clic.
- Hébergement VPS : Pour les sites Web nécessitant plus de puissance et de contrôle, l’hébergement de serveur privé virtuel (VPS) fournit des ressources dédiées au sein d’un environnement partagé. Cette option offre des performances améliorées, un accès root et la possibilité de mettre à l’échelle les ressources au fur et à mesure que votre site se développe.
- Hébergement dédié : Pour les sites Web à grande échelle ou ceux à fort trafic, l’hébergement dédié fournit un serveur entier dédié à votre site. Cela garantit des performances, un contrôle et une sécurité maximum, avec un accès root complet et des configurations de serveur personnalisables.
- Hébergement cloud : L’hébergement cloud de Bluehost est conçu pour la vitesse et la fiabilité, avec un SLA de disponibilité de 100 % et des performances de haut niveau. Il est particulièrement adapté aux agences et aux entreprises à la recherche de solutions d’hébergement évolutives et résilientes.
- Hébergement WordPress : Conçus spécifiquement pour les utilisateurs de WordPress, ces plans d’hébergement WordPress optimisés pour la performance et la sécurité. Il comprend des fonctionnalités telles que les mises à jour automatiques de WordPress, un environnement de staging et un support spécialisé.
- Hébergement WooCommerce : Pour ceux qui cherchent à créer une boutique en ligne, Bluehost propose des plans d’hébergement WooCommerce qui offrent des capacités de boutique en ligne sécurisées avec des outils intégrés pour vous aider à configurer et à gérer efficacement votre site de commerce électronique.
Chaque plan d’hébergement est conçu pour répondre à différents besoins, ce qui garantit que, que vous démarriez un blog, lanciez une boutique en ligne ou développiez un site Web complexe, Bluehost dispose d’une solution pour vous aider à atteindre vos objectifs.
En combinant l’enregistrement de domaine avec un plan d’hébergement approprié, Bluehost rationalise le processus d’établissement d’une présence en ligne robuste et efficace, soutenue par des performances fiables et un support complet.
Réflexions finales
Comprendre la distinction entre les domaines et les sites Web est fondamental pour établir une présence en ligne réussie. Votre domaine agit comme votre adresse numérique, guidant les visiteurs vers votre site Web, la plate-forme où résident votre contenu, vos produits, vos mots-clés ou vos services.
Pour intégrer ces éléments de manière transparente, envisagez de vous associer à un fournisseur fiable. Avec Bluehost, vous pouvez sécuriser sans effort le domaine de votre choix et sélectionner un plan d’hébergement qui correspond à vos besoins spécifiques. Nos services complets et nos outils conviviaux facilitent l’utilisation, le lancement et la gestion de votre site Web, garantissant une expérience sans faille pour vous et vos visiteurs.
Faites le premier pas vers l’établissement de votre présence en ligne en explorant les offres de Bluehost dès aujourd’hui . Que vous démarriez un blog personnel, que vous lanciez une boutique en ligne ou que vous créiez un portfolio professionnel, Bluehost fournit les ressources et le soutien pour vous aider à réussir dans le paysage numérique.
Foire aux questions
The first step is usually buying a domain name. Your domain is your online identity and securing it early ensures that no one else takes it. Once you have a domain, you can then choose a hosting plan and start building your website.
No, a domain name is just the address that directs users to your website. Your website consists of the actual content, files and data stored on a web hosting server.
A domain name is the address that users type in their browser to visit your site, while web hosting is the service that stores your website’s files and makes them accessible online.
Yes, a domain can exist without a website. Many people register domain names for future use, email addresses or brand protection. Similarly, a website can exist without a custom domain by using a hosting provider’s subdomain, but having a unique domain improves credibility and branding.



Ecrire un commentaire