Key highlights
- Learn how to secure a domain name to protect your brand identity and online presence.
- Understand essential domain security measures to prevent hijacking, unauthorized transfers and misuse.
- Explore practical steps for protecting a domain, including locks, authentication and automatic renewals.
- Build a reliable domain security strategy by choosing trusted, ICANN-accredited registrars.
- Keep your domain safe to safeguard users, sensitive data and long-term brand reputation.
Your domain name is your brand’s identifier among millions of websites worldwide. Much like a business address allows people to find your brand’s physical headquarters, your domain name is a primary touchpoint for people online.
For the same reason, your domain name is a prime target for cybercriminals. A 2023 International Data Corporation report shows that organizations suffer an average of 7.5 domain name server attacks each year, with 90% of organizations affected. Without proper domain security, a single attack can lead to traffic loss, data exposure or even complete loss of domain control.
In this guide, you’ll explore why domain name security is essential, the most common threats that put domains at risk and proven, practical steps to secure a domain name and protect your brand for the long term.
How does stronger domain security protect your brand?

According to the 2021 Epik data breach, researchers found that attackers successfully hijacked or took over 8,000 domains and 13,000 subdomains belonging to well-known brands such as eBay, Lacoste, Marvel, McAfee, MSN, Pearson, PwC and The Economist. These hijacked domains were used in spam operations, damaging brand visibility and redirecting users away from legitimate sites.
This is exactly why securing your domain matters. A well-protected domain helps prevent misuse, keeps visitors on the right site and ensures your brand remains visible, trusted and under your control. When your domain is secure, your online presence works the way it’s supposed to
That’s only possible with a secure domain name. In particular, here’s what you’ll enjoy after thoroughly securing your domain.
1. Stronger brand image
Your domain name is closely tied to how people perceive your brand online. When it’s secure, it signals professionalism, credibility and responsible business practices. Customers may not actively think about domain security, but they expect your website and emails to work reliably and lead them to the right place.
Strong domain security also helps prevent misuse such as impersonation, malicious redirects or spam campaigns that abuse your brand name. By keeping control of your domain, you protect your brand’s reputation and ensure that customers associate your name with trust, not risk.
Also read: Small Business Branding- How to Build a Memorable Brand
2. Secure trusted data
A secure domain name plays an important role in protecting both business and user data. When attackers gain control of a domain, they can intercept emails, redirect users to fake pages or exploit trust to steal sensitive information.
The impact of data breaches can be severe. According to a 2025 IBM study, the average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million, factoring in recovery efforts, downtime and lost customer confidence. Strengthening domain security reduces the chances of these incidents by limiting unauthorized access and preventing attackers from exploiting your domain as an entry point.
3. Website availability and business continuity
Your domain is essential for keeping your website accessible. If it’s compromised, your site can become unreachable, redirected or taken offline entirely. Even short periods of downtime can disrupt operations, frustrate users and result in lost sales.
By securing your domain name, you lower the risk of attacks that interfere with DNS settings or domain ownership. This helps keep your website online and available to users, supporting smooth business operations and minimizing unexpected interruptions.
Also read: Register Unique Domains with Bluehost Domain Name Generator
4. Financial stability
Cyberattacks often lead to significant financial consequences, both direct and indirect. When a domain is compromised, attackers may demand ransom payments to restore access or exploit the domain to generate illicit revenue.
In 2024 alone, ransomware victims collectively paid attackers more than $1 billion, according to Chainalysis. Beyond ransom, downtime can be extremely costly.
For example, insider-driven breaches have caused massive financial damage in recent years. In 2025, a social-engineering and ransomware attack linked to insider access disruptions at Marks & Spencer led to an estimated £3.8 million in daily revenue losses, hundreds of millions of pounds in total financial impact and a £750 million drop in market value within days.
On top of this, businesses may face legal expenses, recovery costs and brand repair efforts. Strong domain security helps reduce these risks and supports long-term financial stability.
5. Trust and loyal customers
Trust is a key factor in building and maintaining customer relationships. When your domain is secure, it reassures users that they are interacting with the legitimate website and that their data is being handled responsibly.
Customers are more likely to return, engage and stay loyal to brands that feel safe and reliable. Securing your domain helps reinforce that sense of trust, protecting not just individual interactions but the long-term relationship between your brand and your audience.
6. Compliance with regulations
For businesses in certain sectors, increasing domain security is an integral part of complying with industry regulations around data protection and privacy. This helps you avoid potential legal penalties.
For example, failure to comply with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) 4.0 can lead to fines of between $5,000 and $100,000 per month until you achieve compliance. Meanwhile, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) violations can result in fines of up to €20 million ($21.7 million USD) or 4% of your brand’s annual revenue, whichever is higher.
In contrast, complying with industry regulations positions your brand as a responsible and trustworthy entity in your industry, which makes domain name security a must.
Most common domain name threats that put your website at risk

Understanding the most common domain name threats is the first step toward protecting your website. When you know how attackers exploit domains, it becomes much easier to spot risks early and take the right steps to keep your site secure and under your control.
Here are some of the most common domain name threats you should be aware of.
1. Domain hijacking
Domain hijacking happens when an unauthorized person gains access to your registrar account and takes control of your domain without permission. This is one of the most serious domain-related threats because it gives attackers full control over how your domain is used.
Cybercriminals can accomplish this in several ways, including phishing techniques and exploiting security vulnerabilities in your domain registrar.
Once they have control of your domain, they can do anything they want with it. Sometimes, they redirect traffic to fraudulent websites. At other times, they hold a domain for ransom, demanding payment to restore access.
2. Cybersquatting & typosquatting
Cybersquatting is when a scheming individual registers a domain name likely to be mistaken for a known brand, trademark or person. For example, some malicious actors register misspelled variants of a popular domain name.
Cybersquatters hope to exploit people who think they are visiting a brand’s actual website.
From there, the malicious actor can get unaware users to input their financial info or personal identifiers. Alternatively, a cybersquatter can aim to damage a brand’s reputation by publishing unsavory content while disguised as the brand.
Lastly, malicious actors sometimes aim for profits by selling the domain name to the trademark owner, who would feel pressured to end the misuse.
3. Domain Name System (DNS) attacks
The Domain Name System (DNS) is basically a phonebook for the Internet. We’re familiar with domain names like facebook.com and youtube.com; well, each corresponds to a numerical IP address. The DNS reveals which domain names are associated with each IP address.
DNS attacks can take several forms. For example, there’s domain spoofing, where attackers divert traffic from a legitimate server to a bogus one. From there, they can steal personal data or introduce malware.
Another type of DNS exploit is called distributed denial of service (DDoS), where an attacker floods a server with requests, overwhelming it and ultimately making it inaccessible.
While it helps to be aware, you don’t need to know every possible DNS attack. It’s more efficient to understand how to secure your domain name.
4. Expired domain takeover
If you haven’t thought ahead to when your domain name expires, you’re open to this cybercrime. A bad actor can patiently wait for the expiration, then swiftly purchase your domain before you can renew, thus taking over your online identity.
From there, they could attempt to sell the domain back to you at a profit. Alternatively, they can use your domain for schemes, capitalizing on its existing traffic and established search engine optimization (SEO).
That sounds scary, but we’re confident you’ll never be in that position if you implement the following best practices. These practices protect your domain from web attacks and also safeguard your web browsers.
Also read: Understanding the Different Types of Domain Locks
How to secure a domain name step by step
Here’s a clear, step-by-step guide on how to secure a domain name effectively and protect it from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Choose a trustworthy registrar
- Lock your domain name
- Protect your privacy
- Secure DNS and email authentication
- Use strong, unique passwords
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Register your domain for multiple years
- Set up automatic renewal
- Regularly update your contact information
- Register domain name variants
- Trademark your name
Let’s understand each step in depth and grant you a clear path to securing your domain.

1. Choose a trustworthy domain registrar
The first step to securing your domain name is to choose a reputable domain registrar. You’ll discover many registrars and web hosts online, but not all are created equal.
Look for a provider with a reputation for robust security measures, excellent customer service and a strong track record of defense against cyber threats. Positive reviews and ratings on comparison websites or user review websites, like Trustpilot, are a good sign.
Go for a provider that offers extra domain safety services. For example, Bluehost offers domain locking and privacy protection. Check whether each provider is accredited by a recognized governing body such as the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
If you plan to purchase multiple domains, consider using the same registrar; it will be easier to keep tabs on all your domain names, which in turn makes it easier to detect suspicious activity. It’s also important to choose a registrar that offers built-in protections such as domain locking, WHOIS privacy and account security features. For example, Bluehost includes domain lock by default and offers domain privacy protection to help keep personal information secure.
Also read: WHOIS Domain Lookup for Agencies: Master Registration & Security
2. Lock your domain name
After registering a domain name, enable domain locking. This security feature automatically blocks any domain transfer attempts. Any time you visit the registration website to change account settings or domain settings, verify that domain locking is still on.
When you register a domain with Bluehost, domain lock is enabled by default, helping protect against unauthorized transfers. It’s still a good habit to periodically check that the lock remains active, especially after making account changes.
3. Protect your WHOIS privacy
ICANN requires all domain name owners to provide personal details, your name, email, phone number and address. This information is then displayed publicly on a database called WHOIS.
Everyone, including scammers and hackers, can access the WHOIS database and see personal information linked to each site.
That’s where domain privacy protection comes in; this security feature replaces your sensitive personal information with generic information. This way, you keep your identity secure while complying with ICANN’s domain registration requirements.
With Bluehost, you can enable domain privacy protection directly from your account dashboard, helping keep your identity private while remaining ICANN-compliant.
Keep in mind that privacy protection isn’t available for all top-level domain extensions (TLDs). For example, most country-code TLDs, like .us, .uk and .ca don’t allow privacy protection on WHOIS. If this applies to you, don’t worry; you can still minimize your risk via the following tips on how to secure your domain name.
4. Secure DNS and email authentication
There are two areas people forget when they talk about “domain security”: DNS integrity and email impersonation. Covering both goes a long way in 2026.
Secure DNS with DNSSEC: DNSSEC adds a verification layer to your DNS records so attackers can’t easily spoof or alter where your domain points. It helps prevent DNS-based redirects to fake sites.
Secure email with SPF, DKIM and DMARC: These DNS records stop scammers from sending email that looks like it’s from your domain.
- SPF says which mail servers are allowed to send for your domain
- DKIM signs your emails so they can’t be quietly changed in transit
- DMARC tells inbox providers what to do when SPF/DKIM fail (quarantine or reject), and helps you track abuse
If your domain is managed in Bluehost, you can add these records from your DNS settings so everything stays in one place.
Also read: How to Set Up SPF Records
5. Use strong, unique passwords
Use unique and strong passwords for your registrar account in order to avoid unauthorized access. Include a mix of letters, numbers and special characters to increase complexity. Avoid using common words.
If you have multiple domains with different registrars, use unique passwords for each. A password manager like LastPass, Dashlane, KeePass or 1Password will help you generate a unique password for each of your accounts and store them securely.
Additionally, consider changing your passwords regularly to minimize risk further.
6. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication secures your domain name by requiring a second form of verification beyond the password. The second verification is typically a code or link from a text message, email or authentication app.
Even if someone were to obtain your username and password, they wouldn’t be able to access your account without the additional verification step. Thus, 2FA is a good way to protect against phishing techniques.
7. Register your domain for multiple years
If your domain name registrar lets you lock in your domain for multiple years, take that option, considering that yearly renewals are a frequent opportunity for domain name takeovers.
As a bonus, you’ll enjoy the convenience and discounted rate on long-term registrations.
Also read: How to Transfer A Domain Name to Us
8. Set up automatic renewal
There’s another way to prevent your domain name from getting taken over during expiration: Set up automatic domain renewal.
Eliminating the need to track the renewal date manually will give you peace of mind that there will be no service outages due to late or missed domain name renewals.
Keep your credit card information current to ensure the auto-renewal process completes seamlessly. If your registrar allows it, provide several forms of payment so that if one fails, another one automatically activates and preserves the continuity of your domain registration.
9. Regularly update your contact information
For the tightest domain security, keep your contact information current with your registrar. This ensures you receive timely notifications about your domain name, such as renewal reminders and security alerts.
Up-to-date contact details are also vital for retrieving access to your account if your login credentials get breached or forgotten.
10. Register domain name variants
Register variations of your domain name, including common misspellings and phonetic equivalents. This prevents others from buying these variants to divert traffic from you or tarnish your brand reputation.
Additionally, consider acquiring your domain across multiple top-level domains such as .com, .net and .org to consolidate your brand presence further and prevent threats like cybersquatting.
Also read: 7 Best .com Alternatives for Domains in 2026 (With Tips)
11. Trademark your name
A trademark reinforces your rights over the domain, making it easier to take legal action against people who attempt to harm your business, steal your belongings or profit from your brand’s reputation by deceiving your customers.
Trademarks also act as a deterrent; malicious actors are less likely to target you for cybersquatting if you have trademark protection. If your domain is eligible for a trademark, it’s worth applying for one.
How Bluehost helps simplify secure domain management
Domain security can get messy pretty fast, especially when you’re juggling renewals, settings and random security emails that don’t always make sense. Bluehost helps by keeping most of the essential domain and site security tools in one place, which honestly makes managing a domain feel far less overwhelming.
Bluehost is also officially recommended by WordPress.org, which is a big reason many site owners choose it in the first place. That recommendation isn’t about flashy features but about reliability, ease of use and solid support for people running WordPress sites day to day. When your domain, hosting and basic security tools work well together, there’s just less room for things to break or get overlooked.
Here’s how Bluehost helps simplify domain management.
1. Centralized domain dashboard
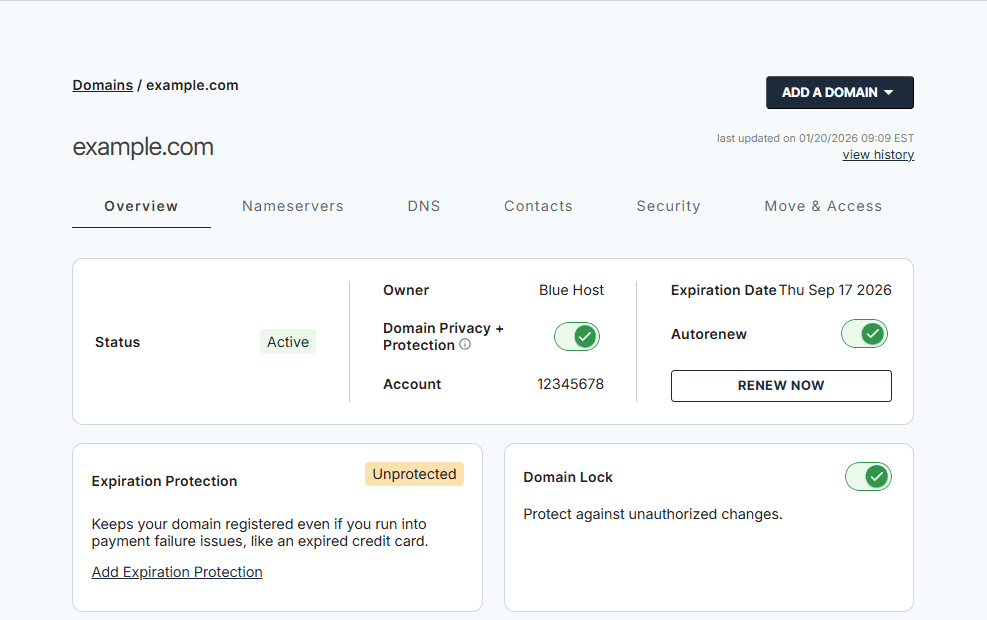
One of the biggest advantages is having everything in a single dashboard. Instead of digging through emails or different tools, you can log in and see your domains, their status and expiration dates right away.
This makes it easier to catch things early, like a domain that’s coming up for renewal or a setting that needs attention. You don’t need to be super technical to understand what’s going on, which is helpful if domain management isn’t something you deal with every day.
2. Built-in domain lock and renewal controls
With Bluehost, domain lock is turned on by default when you register a domain. That means no one can transfer your domain without your approval, which blocks one of the most common takeover methods.
Renewal controls are also straightforward. You can enable auto-renew so your domain doesn’t expire just because you forgot a date or missed an email. It’s a small thing, but it removes a lot of risk that comes from human error.
3. Easy WHOIS privacy and SSL management
By default, domain registration requires your contact information to be public in WHOIS, which isn’t great if you don’t want spam or phishing attempts. Bluehost makes it easy to turn on WHOIS privacy so your personal details aren’t exposed to everyone.
SSL setup is also handled in a way that doesn’t feel overwhelming. While SSL is technically website security (not domain security), it still plays a role in protecting visitors and building trust. Bluehost includes SSL with many hosting plans, so your site traffic stays encrypted without extra setup or confusion.
Also read: Google Security Updates: Why SSL is Essential for Website
4. 24/7 website support
Domain problems usually show up at the worst time. Maybe a renewal didn’t go through or something looks off in your settings. Bluehost offers 24/7 support for domain-related issues, which is useful when you just need someone to help you fix things quickly.
Instead of guessing or searching through help forums, you can reach out and get guidance on domain locks, privacy settings, renewals or transfers. When something feels urgent, having that support makes a real difference.
Domain security checklist for 2026
Domain security is more like a checklist you come back to, especially as threats keep changing and your website grows. If you want to keep your domain protected in 2026, these are the basics you should have covered.
Use this as a quick gut check to see if your domain is actually secure or just looks like it is.
Must-have domain security basics
- Domain lock is enabled: Make sure your domain is locked at the registrar level so it can’t be transferred without your approval. This should always be on.
- WHOIS privacy is active (where available): Your personal contact details shouldn’t be public unless the TLD requires it. Privacy protection helps cut down spam, phishing and social engineering attempts.
- Auto-renewal is turned on: Expired domains are one of the easiest ways for attackers take over websites. Auto-renewal removes the risk of forgetting a renewal date.
- Strong, unique registrar password: Avoid reusing passwords from other services. Your domain account is too important to protect with something weak.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) enabled: This adds a second layer of protection, even if your password is compromised.
- SSL certificate installed and active: SSL doesn’t protect the domain itself, but it does secure traffic to your website and builds trust with visitors. In 2026, an unsecured site is a red flag for users and browsers alike.
- DNS settings reviewed periodically: Check that your DNS records haven’t been changed unexpectedly and still point where they should.
- Contact information kept up to date: Old email addresses or phone numbers can lock you out of important alerts and recovery options.
Smart extras for brands and growing sites
- Multi-year domain registration: Registering for several years reduces renewal risk and shows long-term ownership.
- Common domain variants registered: Misspellings or alternate extensions help prevent lookalike domains and brand misuse.
- Trademark protection (if applicable): A trademark doesn’t stop attacks, but it helps when reclaiming domains or dealing with cybersquatters.
Final thoughts
By now, you’ve got a good handle on how to secure a domain name and why it’s worth paying attention to. A domain might feel like a small detail, but when something goes wrong, it usually turns into a much bigger headache than people expect.
Most domain issues don’t happen because of anything fancy. They happen because of missed renewals, weak account security or settings that were never checked in the first place. Locking your domain, keeping your info private and staying on top of renewals goes a long way in avoiding all of that.
It also helps to use a registrar you can actually rely on. Bluehost has been around for over 20 years and is officially recommended by WordPress.org, which is why a lot of site owners stick with it. Things like domain lock, WHOIS privacy and support that’s available all the time make domain management feel a lot less stressful.
Secure your domain with Bluehost and keep it protected from day one.
FAQs
You cannot permanently own a domain. Domain name registration is leased, usually for 1–10 years. To protect a company’s domain, enable auto-renewal, track the expiration date and keep contact details updated. This ensures a secure domain name over time.
Enable registrar lock and registry lock at the registry level. These stop unauthorized transfers. Add two-factor authentication and privacy tools for extra domain security. Together, these steps are effective for protecting a domain from hijacking or attacks.
Most registrars charge for domain name registration, but some include free domain security tools. Features like WHOIS privacy, SSL certificates and two-factor authentication help create a safe domain. At Bluehost, you also receive a free domain for the first year, with additional features, making it easier to start with strong domain security at no extra cost.
A secure domain name usually costs $10–$50 per year for standard domain name registration. Extra protection, like registry lock or advanced security tools, may increase costs. These add-ons strengthen domain security and reduce risks for your brand or company’s domain.
If you want to know how to secure a domain name, start with a trusted registrar. Use locks at both the registrar and registry levels, enable authentication and protect personal data. Monitor the expiration date and renew early. These actions keep a company’s domain safe.

Write A Comment