Key highlights
- Understand how the different types of SSL certificates offer varying levels of security validation and domain coverage.
- Learn how matching the certificate type to your website’s purpose ensures optimal security without overspending.
- Explore how higher validation levels provide increasing trust signals but require more verification.
- Uncover how domain coverage options determine how many websites you can protect.
- Know how Bluehost offers seamless SSL integration regardless of which type of SSL certificate you choose.
SSL certificates are digital security essentials for every website. They encrypt data between your site and your visitor’s browser to stop hackers from stealing passwords, credit card details and personal information.
Today, SSL is no longer optional. Browsers like Chrome and Firefox show security warnings when a site lacks it. These warnings scare users away, hurting your trust and traffic. But here’s what many site owners miss: there are different types of SSL certificates. Each type offers a specific level of protection and identity verification.
The problem? Many website owners pick the wrong type. They either pay too much for features they don’t need or they choose too little protection for their business. This guide shows you exactly which SSL certificate fits your website. You’ll save money and keep your visitors safe.
But first, let’s make sure you understand the basics.
What is an SSL certificate and what does it do?
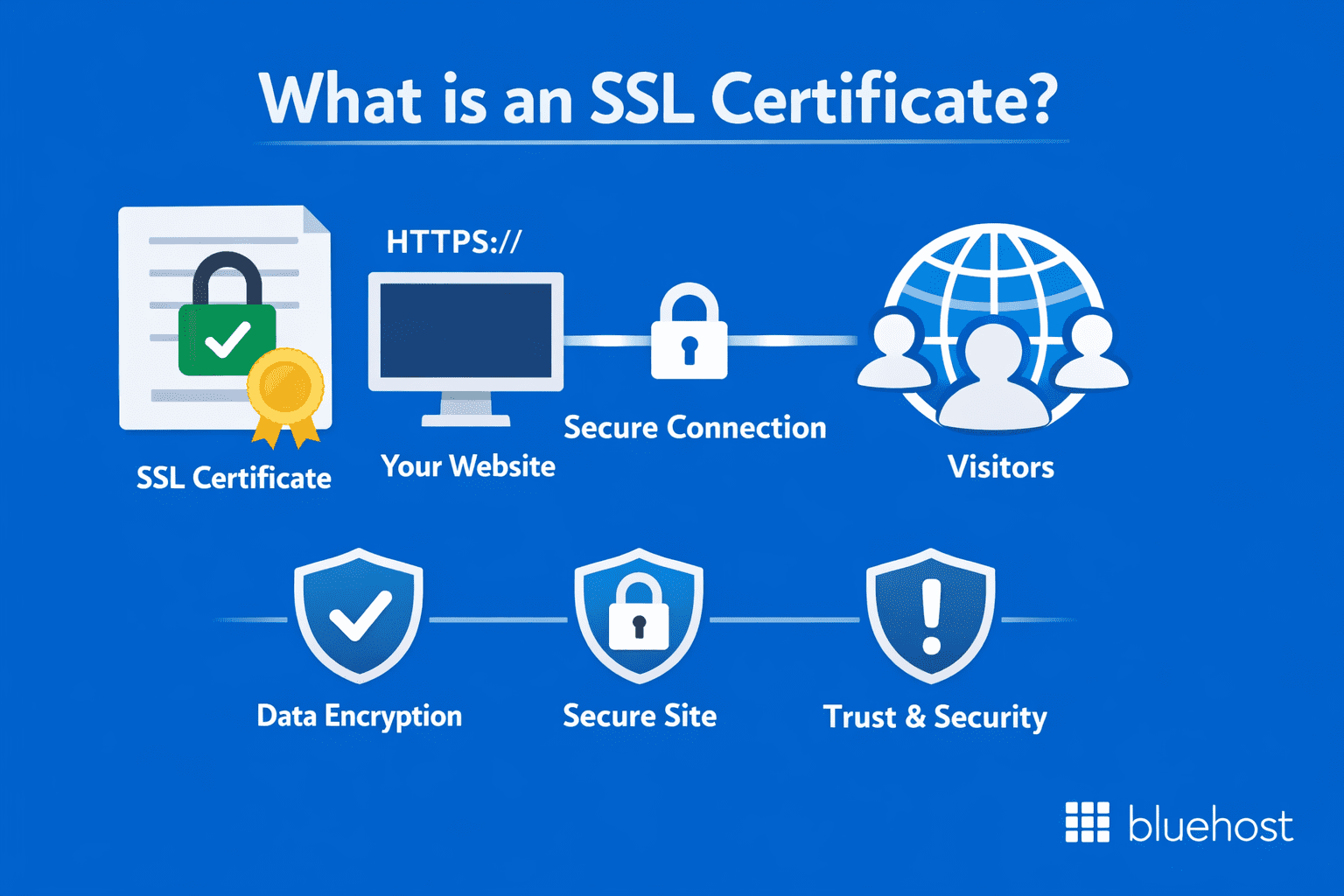
A Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificate creates a secure connection between your website and your visitors’ browsers. Think of it as a digital ID card that verifies your website’s identity while establishing an encrypted connection that protects all exchanged information.
When you install an SSL certificate on your website, it enables the HTTPS protocol (that’s the “https://” at the beginning of web addresses) and activates the padlock icon in browsers. These visual indicators show visitors that your site is secure and trustworthy.
The primary functions of SSL certificates include:
- Encrypting data transmitted between visitors and your website
- Verifying your website’s identity to visitors
- Preventing data theft and unauthorized access
- Building visitor trust through visible security indicators
- Improving search engine rankings (Google favors secure sites)
How do you know when a website is using SSL?
The most obvious sign of SSL protection appears in your web browser’s address bar. Several visual elements indicate that a website has properly implemented SSL security.
Look for these SSL indicators:
- HTTPS before the domain name (instead of HTTP)
- A padlock/tune icon or site controls icon in the address bar (the exact icon varies by browser)
- Certificate details available when you click the icon (you can view who issued the certificate and whether the connection is secure)
- No “Not Secure” label or security warnings when visiting the site
- The site loads normally over https:// and stays on HTTPS as you navigate (no redirect loops or browser interstitial warnings)
Note: Extended Validation (EV) certificates still provide stronger organizational vetting, but most modern browsers (including Chrome and Firefox) do not display a green bar or prominently show the company name in the address bar like they used to. In many cases, EV details are only visible after clicking the address bar icon or viewing certificate information.
To check certificate details:
- Click the padlock icon in your browser’s address bar
- Select “Certificate” or “Connection is secure”
- Review the certificate information, including:
- Issuing Certificate Authority (CA)
- Valid dates and expiration
- Domain name coverage
- Validation level
- Encryption strength
Browsers also alert you when something’s wrong with a website’s SSL implementation. These warnings signal potential security risks that deserve caution.
Also read: How to Get an SSL Certificate (Free or Paid) for WordPress
SSL vs. TLS: Is there a difference?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are technically different. TLS is the modern, more secure successor to the now-deprecated SSL protocols. However, because “SSL” became the industry standard term, it is still widely used to describe these digital certificates even though the underlying technology has evolved to TLS.
Rest assured, you do not need to choose between the two when securing your website. When you purchase an SSL certificate today, you are effectively getting TLS support. Hosting providers like Bluehost automatically configure these certificates to use the latest, most secure TLS protocols, ensuring your website maintains the highest security standards without requiring you to manage complex technical configurations.
SSL certificate validation types: Why the verification level matters?
Before a Certificate Authority (CA) issues an SSL certificate, it verifies the identity behind the request. The depth of that verification, not the encryption strength, is what separates the three validation levels. Choosing the right level is a strategic decision: it determines how much reassurance your site gives to cautious visitors, particularly those about to share payment details or personal data.
Higher validation tells those visitors that your organization has been independently confirmed as legitimate, not just that you own a domain. That distinction can directly influence whether they complete a purchase or abandon your site entirely.
- DV SSL: Verifies domain ownership only; issued in minutes to hours; produces a standard browser padlock with no organization identity behind it.
- OV SSL: Verifies domain control plus business identity and legal existence; issued in 1–3 days; displays verified organization details inside the certificate.
- EV SSL: Verifies domain, legal status, physical address and operational legitimacy through official records; issued in 1–7 days; delivers maximum identity assurance for high-stakes visitor interactions.
Every Bluehost hosting plan includes a free DV SSL, auto-managed through the platform with no manual steps required. When your site collects payments or sensitive customer data, you can upgrade to OV or EV directly through the Bluehost dashboard to match your site’s trust requirements.
Also read: What You Need to Know About SSL Certificates
What are the main types of SSL certificates?

Different types of SSL certificates are available, each designed for specific security needs and website configurations. The following table breaks down the key differences between Domain Validation (DV), Organization Validation (OV) and Extended Validation (EV) certificates:
| Validation type | Validation process | Issuance time | Best for |
| Domain Validation | Email or file verification | Minutes to hours | Blogs, personal sites |
| Organization Validation | Business verification | 1-3 days | Business websites |
| Extended Validation | Legal verification | 1-7 days | eCommerce, banking |
| Hosting environment | Recommended SSL certificate type | Key visitor benefit | Bluehost support level |
| Shared hosting | DV SSL | Padlock icon and encrypted connection from day one | Free, auto-installed via Let’s Encrypt, no manual steps |
| WordPress hosting | DV SSL (managed) | HTTPS active the moment your site launches | One-click SSL activation in the Bluehost dashboard |
| eCommerce / WooCommerce hosting | OV or EV SSL | Verified business identity that increases checkout confidence | Free SSL is generally DV and OV/EV would require buying premium SSL. |
- Shared hosting: A DV SSL is all you need. Every Bluehost shared hosting plan includes a free managed DV SSL certificate powered by Let’s Encrypt, auto-installed and auto-renewed so your visitors always see the padlock icon from day one, with nothing for you to configure.
- Managed WordPress hosting: Bluehost managed WordPress plans configure HTTPS automatically. Your site is secured the moment you launch and one-click SSL activation is visible directly inside your Bluehost dashboard, no plugins or technical steps required.
- WooCommerce hosting: When your store handles payment details or personal customer data, an OV or EV SSL is the stronger choice. Bluehost WooCommerce hosting does provide free SSL certificates, these are generally DV SSLs. To get OV or EV SSL certificates with visible trust indicators at checkout, customers would need to purchase premium SSL certificates from Bluehost.
Which SSL certificate types suit your specific website use case: DV vs OV vs EV SSL?
Choosing the right SSL certificate becomes straightforward once you match it to your actual website situation. The five scenarios below cut through the guesswork, pairing each real-world use case with the correct certificate type and the business outcome that choice delivers.
- Small business service website (law firm, consultant, local contractor): DV or OV SSL. An OV certificate adds verified business identity to your security credentials, giving prospective clients measurable confidence before they contact you — particularly important when visitors are comparing providers and evaluating trustworthiness.
- eCommerce store: OV or EV SSL. Visible trust signals at checkout directly reduce cart abandonment. Bluehost WooCommerce hosting supports seamless premium SSL certificate upgrades, so you can activate higher validation without migrating to a new platform.
- Healthcare provider or legal practice: EV SSL. Patients and clients sharing confidential data expect the highest level of identity verification. EV’s rigorous validation process demonstrates that legitimacy and supports the sensitivity that regulated industries demand.
- Web agency or multi-brand business: Multi-Domain OV or EV SSL. One certificate covering multiple client or brand websites consolidates renewal dates, reduces management overhead and maintains consistent trust signals across every property you oversee.
How do SSL certificates differ by domain coverage?
Beyond validation levels, the types of SSL certificates also differ in how many websites they can protect. The domain coverage of an SSL certificate determines how many websites or subdomains it can protect. Your choice depends on your website structure, future growth plans and management preferences.
Here’s how the three main coverage types compare:
| Coverage type | Protects | Example | Ideal for | Management complexity |
| Single Domain | One domain only | [example].[com] | Simple websites | Low |
| Wildcard | Main domain + all subdomains | [example].[com] | Sites with multiple sections | Medium |
| Multi-Domain | Multiple different domains | [example].[com], [example].[org] | Businesses with several websites | Medium-high |
This comparison highlights how your website structure should guide your certificate selection. Let’s cover each domain coverage certificates in detail:
1. Single Domain SSL certificates
As their name suggests, Single Domain certificates protect exactly one website domain or subdomain. If you secure “[example].[com],” that certificate won’t cover “[shop].[example].[com]” or any other domain variation. It’s a one-domain, one-certificate relationship.
These certificates provide a straightforward and cost-effective solution when you have just one website to secure. Since they cover the minimum necessary, they typically come at the lowest price point among coverage options.
For many website owners, a Single Domain certificate provides all the protection needed without paying for unnecessary coverage.
Key characteristics of Single Domain certificates:
- Protect one domain or subdomain
- Cannot cover additional domains
- Most affordable certificate option
- Straightforward implementation
- Specific, targeted protection
Use cases:
- Small business websites with one domain
- Personal websites and portfolios
- Professional service sites (lawyers, consultants)
2. Wildcard SSL certificates
Wildcard certificates offer much greater flexibility by protecting your main domain and all its first-level subdomains. A certificate for “[example].[com]” automatically covers “[shop].[example].[com],” “[blog].[example].[com],” and any other subdomain you might create at that level.
This versatility allows you to add new subdomains without purchasing additional certificates. For growing websites that frequently expand with new sections or services, Wildcard certificates provide both convenience and cost savings. You’re essentially future-proofing your security setup against expansion.
Also read: What Is a Wildcard SSL Certificate? Setup Guide
Key characteristics of Wildcard certificates:
- Cover unlimited first-level subdomains
- Single certificate for multiple sites
- Higher initial cost than Single Domain
- More cost-effective with many subdomains
- Simplified certificate management
Use cases:
- Growing websites adding new sections
- eCommerce stores with product category subdomains
- Educational sites with department subdomains
3. Multi-Domain SSL certificates
Multi-Domain certificates (also called Subject Alternative Name or SAN certificates) take flexibility even further by protecting multiple domain names with one certificate. A single certificate can secure completely separate domains like “[example].[com],” “[example].[org],” and “[example].[net].”
These certificates are the ultimate solution for businesses managing several distinct websites. Instead of juggling multiple certificates with different renewal dates and management requirements, you handle everything through one comprehensive certificate. You can typically secure up to 250 different domains, depending on your provider.
Key characteristics of Multi-Domain certificates:
- Protect multiple unrelated domains
- Typically cover 3-250 domains (varies by provider)
- Highest initial cost but economical for multiple sites
- Centralized management of all domains
- Single renewal date for all secured websites
Use cases:
- Businesses with multiple brand websites
- Digital agencies managing client websites
- Organizations with country-specific domains (.com, .co.uk, etc.)
Also read: How to Set Up an SSL Certificate for Website Security
What specialized SSL certificates should you know about?
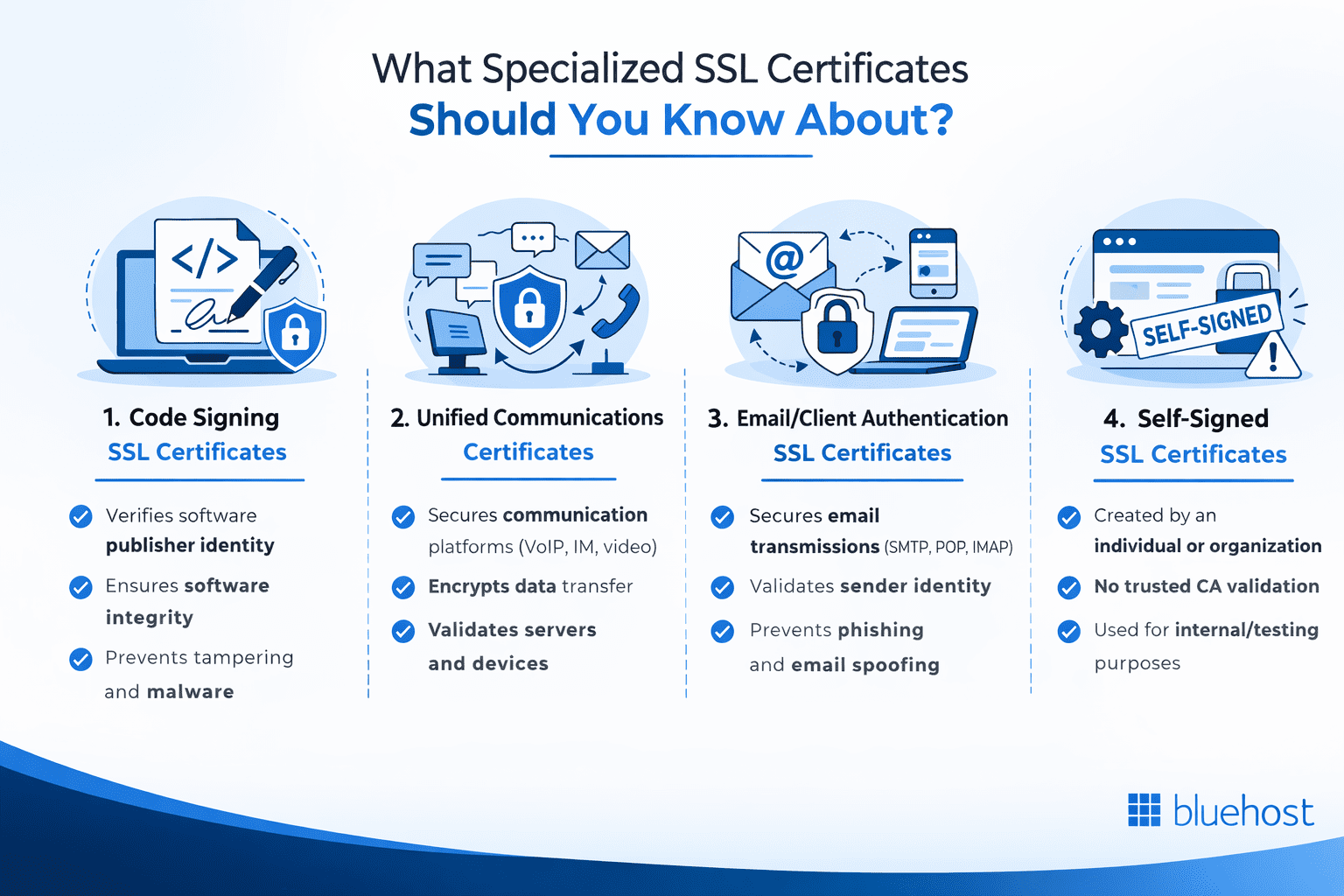
Specialized digital certificates expand beyond website protection to secure other important digital assets and communications. Let’s explore these unique certificate types and their specific applications.
1. Code Signing SSL certificates
When you download software, how do you know it’s safe? That’s where Code Signing certificates come in. Unlike website SSL certificates that secure data transmission, Code Signing certificates verify the identity of software publishers and guarantee their code hasn’t been tampered with.
Key benefits of Code Signing certificates include:
- Verification of software publisher identity
- Confirmation that code hasn’t been modified since signing
- Elimination of security warnings during installation
- Increased user trust and download confidence
- Protection against malware insertion in distribution
When developers sign their applications with these certificates, users receive verification of who created the software. More importantly, the signature confirms the code hasn’t been modified since its creation, no malware insertions or other malicious changes.
Also read: How to Remove Malware From WordPress Site
This verification creates crucial trust between developers and users. When you see that security prompt confirming a program comes from a verified publisher, that’s a Code Signing certificate at work. For software companies, these certificates transform anonymous code into trusted applications that users feel confident installing.
2. Unified Communications Certificates
Unified Communications Certificates (UCC) are specialized Multi-Domain certificates designed specifically for Microsoft Exchange and Office Communications environments. These certificates secure multiple domain names while providing seamless compatibility with communication servers.
UCC is particularly valuable for organizations with integrated email, messaging and collaboration tools.
How UCC protects your collaboration platforms:
- Secure multiple domains and subdomains
- Optimized for Microsoft communication platforms
- Support for both internal and external domain names
- Compatible with Exchange, Skype for Business and other collaboration tools
- Similar validation options as standard certificates (DV, OV, EV)
3. Email/client authentication SSL certificates
Email/client authentication certificates (sometimes called S/MIME certificates) address phishing and spoofing threats by securing email communications and verifying sender identity.
How email/client authentication certificates protect your communications:
- Encrypt email contents to prevent unauthorized access
- Provide digital signatures that verify sender identity
- Protect against email spoofing and phishing attempts
- Enable secure sharing of sensitive information
- Create compliance with data protection regulations
These certificates serve two vital functions. First, they encrypt the contents of emails, ensuring that sensitive information remains private as messages travel across the internet. Second, they provide digital signatures that confirm emails truly come from the claimed sender, not an impersonator.
Also read: Enable SMTP Authentication: Email Troubleshooting
For businesses exchanging confidential information through email, these certificates provide essential protection.
4. Self-signed SSL certificates
Unlike the certificates we’ve discussed so far, self-signed certificates aren’t issued by trusted CAs. Instead, as the name suggests, they’re created and signed by the same entity using them. This fundamental difference affects how browsers and users interpret them.
Appropriate uses for self-signed certificates:
- Development and testing environments
- Internal corporate networks and intranets
- Personal projects not accessible to the public
- Learning and educational environments
- Temporary staging servers
Self-signed certificates provide the same encryption capabilities as CA-issued certificates. Data transmitted between users and websites remains protected from eavesdropping. However, because no trusted third party verifies the certificate creator’s identity, browsers display warning messages when users visit sites using self-signed certificates.
Also read: How to Install a Third-Party SSL Certificate in cPanel
Warning: Never use self-signed certificates on public-facing production websites. The browser warnings create immediate distrust and many users will leave rather than proceed past security alerts. For any commercial website, proper CA-issued certificates remain essential for establishing visitor trust.
Now that you understand all the SSL certificate types available, let’s focus on how to select the perfect one for your specific website needs.
How do you choose the right SSL certificate for your website?
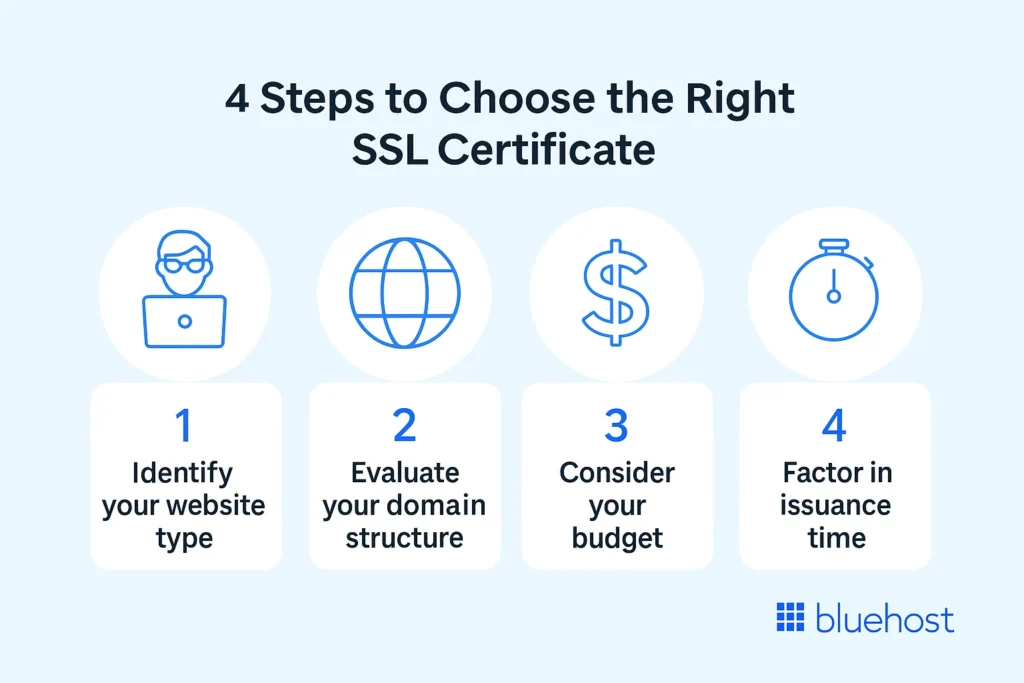
With so many different types of SSL certificates available, you might think selection is challenging. However, by focusing on a few key factors, you can identify the ideal certificate for your specific situation.
Your selection should be SSL certificates based on your specific security needs, website structure and budget considerations
Quick decision checklist:
- What type of website am I securing? (personal, business, eCommerce)
- How many domains and subdomains need protection?
- What’s my budget for website security?
- How quickly do I need the certificate issued?
- What level of visitor trust does my site require?
1. Consider your website type and purpose
The nature of your website largely determines what level of validation you need. Different websites require different levels of visitor trust and your SSL certificate should match those requirements.
Match your website type to the appropriate validation level:
- Blogs and personal sites: Domain Validation
- Business websites and professional services: Organization Validation
- eCommerce and financial services: Extended Validation
- Healthcare portals: Extended Validation
- Educational resources: Domain or Organization Validation
2. Evaluate your domain structure
Your website’s current structure and future expansion plans should guide your choice between Single Domain, Wildcard and Multi-Domain certificates.
Domain structure decision guide:
- Single website with no subdomains: Single Domain certificate
- Main domain with multiple subdomains: Wildcard certificate
- Several different domain names: Multi-Domain certificate
- Complex mix of domains and subdomains: Combination of Wildcard and Multi-Domain
3. Balance security needs with budget constraints
SSL certificates vary significantly in price based on validation level, domain coverage and CA. While security should never be compromised, finding the right balance between protection and cost makes good business sense.
Typical price ranges and value considerations:
- Domain Validation: $0-30/year – Best value for basic websites
- Organization Validation: $40-100/year – Middle ground for business sites
- Extended Validation: $100-300/year – Premium option for high-trust needs
- Wildcard certificates: 2-5× the price of Single Domain – Cost-effective with 3+ subdomains
- Multi-Domain certificates: Base price plus per-domain fee – Economical for multiple websites
When evaluating costs, consider not just the certificate price but also the potential business impact.
Note: SSL certificate prices and values mentioned are based on public data as of 2026 and may vary by provider, features and promotions. For the latest pricing, check with the official SSL providers or your hosting company.
4. Factor in issuance time
Sometimes security implementation timelines matter, particularly for new websites or those transitioning from HTTP to HTTPS. Different certificate types require varying processing periods.
Certificate issuance timeframes:
- Domain Validation: Minutes to hours (fastest option)
- Organization Validation: 1-3 days (moderate processing time)
- Extended Validation: 1-7 days (longest verification period)
- Renewal processing: Usually faster than initial issuance
Once you’ve determined which certificate type best suits your needs, the next important decision is where to purchase it from. This choice significantly impacts your experience.
Also read: A Must-Have Website Security Checklist
Understanding SSL warranties
An SSL warranty acts as an insurance policy provided by the Certificate Authority (CA) to protect you financially. If a CA fails to properly validate a fraudulent certificate or issues one to an unauthorized party, this warranty covers damages resulting from that mis-issuance. It does not cover security breaches caused by your own lapses, such as weak passwords, but offers a safety net specifically against the issuer’s failure.
While free DV certificates usually come with no financial warranty, paid OV and EV certificates often include substantial protection ranging from $10,000 to over $1,000,000. For high-transaction eCommerce sites, this added financial protection is a key factor in choosing a paid certificate. It provides critical liability coverage that free options simply cannot match, ensuring your business is protected against unlikely but costly verification errors.
Why should you buy your SSL certificate from Bluehost?
When it comes to SSL certificates, where you purchase them matters almost as much as which type you choose. While many providers sell SSL certificates, buying from your hosting company offers distinct advantages.
Here’s why Bluehost stands out as your ideal SSL certificate provider.
1. Seamless integration with your hosting environment
Purchasing an SSL certificate from Bluehost keeps your hosting, domain and security in one place. That tighter integration helps reduce common setup issues that can happen when you buy a certificate elsewhere and then try to install it manually.
Benefits of Bluehost’s integrated approach:
- SSL managed alongside your hosting and domain tools
- Automatic installation for many Domain Validation (DV) certificates (depending on your plan and setup)
- Less manual configuration compared to many third-party installs
- One dashboard to manage key website components
- Streamlined renewal and visibility into certificate status
Note: Some certificate types and configurations may still require additional verification steps (and in certain cases a CSR). Bluehost provides guided setup and documentation for these scenarios.
Also read: How to Create Certificate Signing Request
2. Trusted by millions and recognized in the WordPress ecosystem
Bluehost is widely used across the web and is a familiar name for site owners who want dependable hosting and website security. If you’re building with WordPress, Bluehost is also listed on WordPress.org’s recommended hosting page, which makes it a common starting point for new WordPress sites.
That trust matters because SSL isn’t just a technical checkbox, your certificate is part of how visitors and browsers judge whether your site is safe.
Also read: Bluehost Review 2026: Is Bluehost Still Worth It for Websites Today?
3. Support when SSL issues get complicated
Even with an easier setup, SSL questions can come up, especially when you’re migrating an existing site to HTTPS, fixing mixed content warnings, or configuring multiple domains and subdomains.
With Bluehost, you can get help from a support team that understands both SSL certificates and the Bluehost hosting environment, which can speed up troubleshooting compared to using a third-party certificate provider.
4. Simple SSL management through your Bluehost dashboard
Managing your SSL certificate is easier when it lives in the same place as your hosting tools. Bluehost’s control panel helps you keep track of your certificate and make changes without juggling multiple vendors.
You can typically handle tasks like:
- Checking certificate status and coverage
- Getting renewal reminders and managing renewals
- Installing or activating SSL for supported domains
- Upgrading certificate types when your site grows (e.g., adding subdomains or expanding coverage)
Don’t leave your website security to chance. Explore our WordPress hosting options today and secure your online presence with confidence.
Final thoughts
The right SSL certificate protects data while signaling trustworthiness to visitors. Your choice should reflect your website’s purpose:
- DV certificates for personal sites
- OV for professional businesses
- EV for financial or eCommerce platforms where trust directly impacts your bottom line.
Don’t let technical complexity prevent you from securing your site properly. Bluehost transforms SSL implementation from a technical headache into a simple checkbox in your website setup. Our seamless installation, 24/7 expert support and competitive pricing make website security accessible for every site owner, regardless of technical background.
Secure your website with Bluehost today!
FAQs
SSL certificates come in several formats, with PEM being the most common. Other formats include DER, PFX/PKCS#12 and JKS. Most servers use PEM format, which appears as Base64 encoded text with .crt, .pem or.key extensions.
To identify your SSL certificate type, click the padlock icon in your browser’s address bar and select “Certificate.” Check for “Validation Type” or examine the Subject field. DV certificates show only domain information, OV certificates include organization details and EV certificates display comprehensive company information. You can also view certificate details in your Bluehost control panel.
Free SSL certificates provide the same encryption strength as paid certificates, creating equally secure HTTPS connections. However, they typically offer only Domain Validation without additional features like warranties or higher validation levels. Free certificates work well for basic blogs and informational sites, while business websites and eCommerce stores benefit from paid certificates with stronger trust signals.
Yes, you can upgrade from a Domain Validation (DV) to an Extended Validation (EV) certificate. This requires purchasing a new certificate with higher validation rather than updating your existing one. You’ll need to submit additional documentation to verify your organization’s identity. With Bluehost, certificate upgrades are straightforward through your control panel, with our support team guiding you through the necessary steps.



Write A Comment